Form the differential equation representing family of curves given by (x – a)² + 2y²= a², where a is an arbitrary constant.
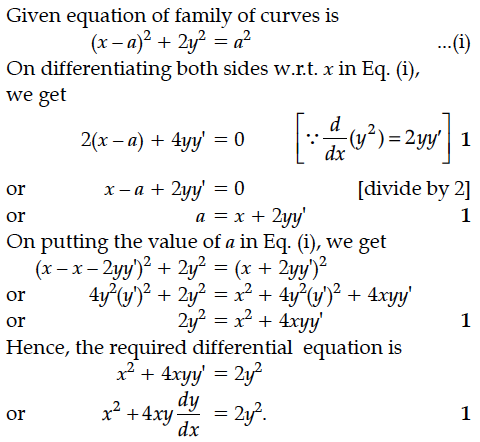
Find the differential equation representing the family of curves where A and B are arbitrary constants.
Form the differential equation representing family of ellipses having foci on X-axis and centre at the origin.
From the differential equation of equation y = a cos 2x + b sin 2x, where a and b are constant.
Write the differential equation formed from the equation y = mx + c, where m and c are arbitrary constants.
Form the differential equation of the family of circles in the second quadrant and touching the co-ordinate axes.
Form the differential equation of all circles which is tough the x-axis at the origin.
Show that the relation R on the set Z of all integers defined by (x, y) ∈ is divisible by 3 is an equivalence relation.
A bag contains (2n + 1) coins. It is known that (n – 1) of these coins have a head on both sides, whereas the rest of the coins are fair. A coin is picked up at random from the bag and is tossed. If the probability that the toss results in a head is 31/42, determine the value of n.
Assume that each born child is equally likely to be a boy or a girl. If a family has two children, what is the conditional probability that both are girls ? Given that :
(i) the youngest is a girl.
(ii) atleast one is a girl.
If y(x) is a solution of the differential equation then find the value of
The total expenditure (in ₹) required for providing the cheap edition of a book for poor and deserving students is given by R(x) = 3x² + 36x, where x is the number of set of books. If the marginal expenditure is defined as write the marginal expenditure required for 1200 such sets.
Probability of solving specific problem independently by A and B are 1/2 and 1/3 respectively. If both try to solve the problem, independently, then find the probability that
(i) the problem is solved
(ii) exactly one of them solves the problem
