Draw a plot showing the variation of resistivity of a (i) conductor and (ii) semiconductor, with the increase in temperature. How does one explain this behaviour in terms of number density of charge carriers and the relaxation time ?
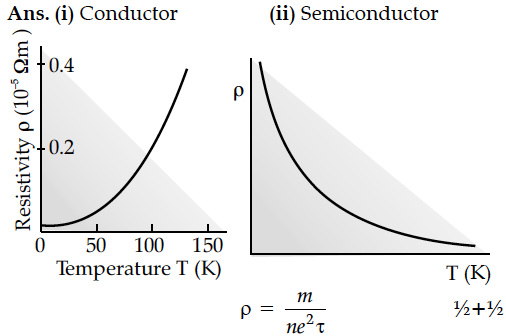
In conductors, average relaxation time decreases with increase in temperature, resulting in an increase in resistivity.
In semiconductors, the increase in number density (with increase in temperature) is more than the decrease in relaxation time; the net result is, therefore, a decrease in resistivity.
What is relaxation time ? Derive an expression for resistivity of a wire in terms of number density of free electrons and relaxation time.
Draw a graph showing variation of resistivity with temperature for nichrome. Which property of nichrome is used to make standard resistance coils ?
Draw a graph to show the variation of resistance of a metal wire as a function of its diameter keeping its length and material constant.
Graph showing the variation of current versus voltage for a material GaAs is shown in the figure, identify the region of :
A 10 V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a 200 V battery and a resistance of 38Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of the current in the circuit.
Plot a graph showing the variation of current I versus resistance R, connected to a cell of emf E and internal resistance r.
How does the random motion of free electrons in a conductor get affected when a potential difference is applied across its ends ?
Show that the current leads the voltage in phase by in an ac circuit containing an ideal capacitor.
Two closely spaced equipotential surfaces A and B with potentials V and V + , (where is the change in V), are kept distance apart as shown in the figure. Deduce the relation between the electric field and the potential gradient between them. Write the two important conclusions concerning the relation between the electric field and electric potentials.
Two charges q and –3q are placed on x-axis separated by distance d. Where a third charge 2q should be placed such that it will not experience any force ?
Five charges, q each are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side a.
(i) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed ?
(ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by - q ?
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2.5 × 10⁻⁷ m² carrying a current of 1.8 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 10²⁸ m⁻³.
A capacitor ‘C’, a variable resistor ‘R’ and a bulb ‘B’ are connected in series to the ac mains in circuit as shown. The bulb glows with some brightness.How will the glow of the bulb change if
(i) a dielectric slab is introduced between the plates of the capacitor, keeping resistance R to be the same;
(ii) the resistance R is increased keeping the same capacitance ?
An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field with its dipole moment parallel to the field. Find
(i) the work done in turning the dipole till its dipole moment points in the direction opposite to .
(ii) the orientation of the dipole for which the torque acting on it becomes maximum.
