Five charges, q each are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side a.
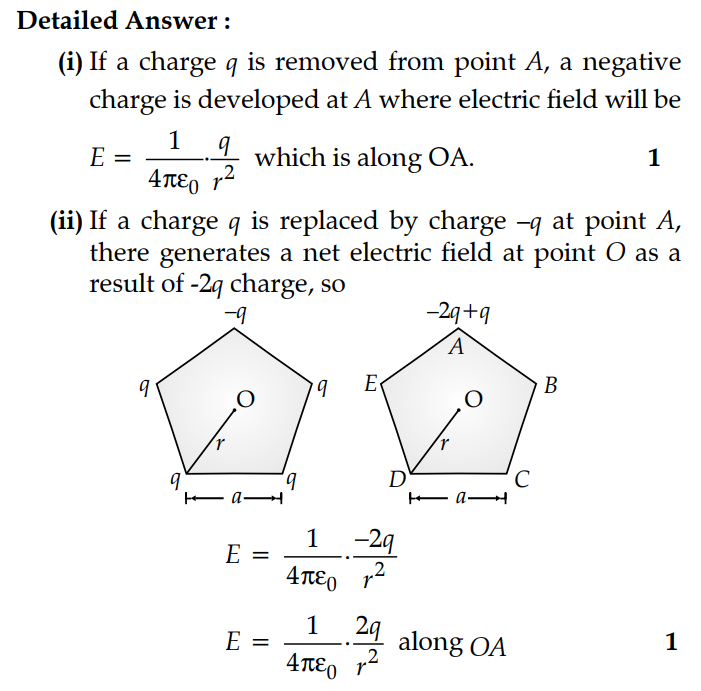
(i) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed ?
(ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by - q ?
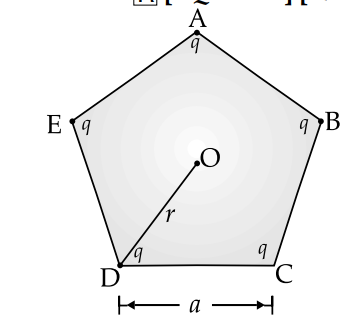
(i) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed ?
(ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by - q ?


A charge + Q, is uniformly distributed within a sphere of radius R. Find the electric field, due to this charge distribution, at a distant point r from the centre of the sphere where :
(i) 0 < r < R
(ii) r > R
There is a point charge q located at the center of a cube. What is the electric flux of this point charge, through a face of the cube?
(A)q/ε₀
(B) q/6ε₀
(C) q/3ε₀
(D)It will depend upon the size of the cube
Figure shows a point charge + Q, located at a distance R/2 from the centre of a spherical metal shell. Draw the electric field lines for the given system.
Three charges each equal to 2 μC are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle. If force between any two charges is 2F, then the net force on either will be:
(i) Derive the expression for electric field at a point on the equatorial line of an electric dipole.
(ii) Depict the orientation of the dipole in (i) stable, (ii) unstable equilibrium in a uniform electric field.
A point charge +Q is placed in the vicinity of a conducting surface. Draw the electric field lines between the surface and the charge.
Two charges q and –3q are placed on x-axis separated by distance d. Where a third charge 2q should be placed such that it will not experience any force ?
Write two properties of equipotential surfaces. Depict equipotential surfaces due to an isolated point charge. Why do the equipotential surfaces get closer as the distance between the equipotential surfaces and the source charge decreases ?
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the conditions under which
(i) the impedance of the circuit is minimum, and
(ii) wattless current flows in the circuit.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected to two external resistances R₁ and R₂ and a perfect ammeter. The current in the circuit is measured in four different situations :
(i) without any external resistance in the circuit
(ii) with resistance R1 only
(iii) with R1 and R2 in series combination
(iv) with R1 and R2 in parallel combination.
The currents measured in the four cases are 0.42 A, 1.05 A, 1.4 A and 4.2 A, but not necessarily in that order. Identify the currents corresponding to the four cases mentioned above.
Calculate the current drawn from the battery by the network of resistors shown in the figure.
A small metallic sphere carrying charge +Q is located at the centre of a spherical cavity in a large uncharged metallic spherical shell. Write the charges on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell. Write the expression for the electric field at the point P1.
A battery of emf E and internal resistance, r, when connected with an external resistance of 12Ω produces a current of 0.5 A. When connected across a resistance of 25Ω, it produces a current of 0.25 A. Determine
(i) the emf and (ii) the internal resistance of the cell.
A network of resistors is connected to a 16 V battery with internal resistance of 1 Ω, as shown in the following figure. Compute the equivalent resistance of the network.
