An inductor of 200 mH, capacitor of 400 µF and a resistor of 10 Ω are connected in series to ac source of 50 V of variable frequency. Calculate the
(a) angular frequency at which maximum power dissipation occurs in the circuit and the corresponding value of the effective current, and
(b) value of Q-factor in the circuit.
(a) angular frequency at which maximum power dissipation occurs in the circuit and the corresponding value of the effective current, and
(b) value of Q-factor in the circuit.
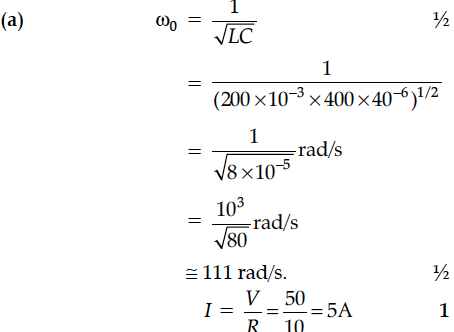
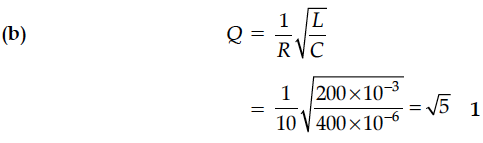
The figure shows a series LCR circuit with L = 5.0 H, C = 80 µF, R = 40 Ω connected to a variable frequency of 240 V source. Calculate
A voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipate over a cycle.Under what conditions is
(i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit,
(ii)maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?
A source of ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
A circuit containing an 80 mH inductor and a 250 µF capacitor in series connected to a 240 V,100 rad/s supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible.
(i) Obtain rms value of current.
(ii) What is the total average power consumed by the circuit ?
A source of ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is connected to a series combination of a resistor ‘R’ and a capacitor ‘C’. Draw the phasor diagram and use it to obtain the expression for
(i) impedance of the circuit and
(ii) phase angle.
A sinusoidal voltage of peak value 10 V is applied to a series LCR circuit in which resistance,capacitance and inductance have values of 10 Ω,1 µF and 1 H respectively. Find
(i) the peak voltage across the inductor at resonance
(ii) quality factor of the circuit.
The figure shows a series LCR circuit connected to a variable frequency of 200 V source with L = 50 mH, C = 80 µF and R = 40 Ω find.
(i) the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance;
(ii) the quality factor (Q) of the circuit.
Two material bars A and B of equal area of crosssection, are connected in series to a DC supply. A is made of usual resistance wire and B of an n-type semiconductor.
(i) In which bar is drift speed of free electrons greater?
(ii) If the same constant current continues to flow for a long time, how will the voltage drop across A and B be affected?
Justify each error.
A voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipate over a cycle.Under what conditions is
(i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit,
(ii)maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?
(i) Derive the expression for electric field at a point on the equatorial line of an electric dipole.
(ii) Depict the orientation of the dipole in (i) stable, (ii) unstable equilibrium in a uniform electric field.
The following table gives the length of three copper wires, their diameters, and the applied potential difference across their ends. Arrange the wires in increasing order according to the following :
(i) The magnitude of the electric field within them,
(ii) The drift speed of electrons through them, and
(iii) The current density within them.
Define an equipotential surface. Draw equipotential surfaces :
(i) in the case of a single point charge and
(ii) in a constant electric field in z-direction. Why the equipotential surfaces about a single charge are not equidistant ?
(iii) Can electric field exist tangential to an equipotential surface ? Give reason.
(i) The potential difference applied across a given resistor is altered so that the heat produced per second increases by a factor of 9. By what factor does the applied potential difference change ?
(ii) In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 W are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 W. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
Derive the expression for the average power dissipated in a series LCR circuit for an ac source of a voltage, V = sin ωt , carrying a current,i = sin (ωt + Φ)
Hence define the term “Wattless current”. State under what condition it can be realized in a circuit.
