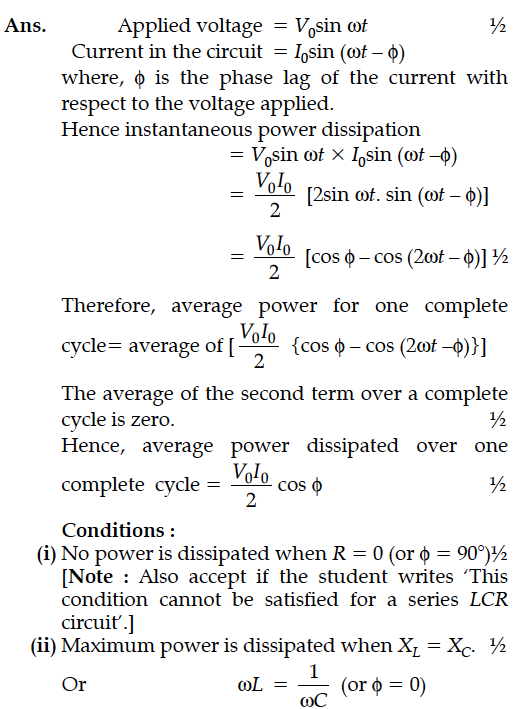
A voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipate over a cycle.Under what conditions is
(i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit,
(ii)maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?
(i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit,
(ii)maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?
An ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is applied to a pure inductor L. Obtain an expression for the current in the circuit. Prove that the average power supplied to an inductor over one complete cycle is zero.
A source of ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the conditions under which
(i) the impedance of the circuit is minimum, and
(ii) wattless current flows in the circuit.
A sinusoidal voltage of peak value 10 V is applied to a series LCR circuit in which resistance,capacitance and inductance have values of 10 Ω,1 µF and 1 H respectively. Find
(i) the peak voltage across the inductor at resonance
(ii) quality factor of the circuit.
A lamp is connected in series with a capacitor. Predict your observation for dc and ac connections. What happens in each if the capacitance of the capacitor is reduced ?
A circuit containing an 80 mH inductor and a 250 µF capacitor in series connected to a 240 V,100 rad/s supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible.
(i) Obtain rms value of current.
(ii) What is the total average power consumed by the circuit ?
A source of ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is connected to a series combination of a resistor ‘R’ and a capacitor ‘C’. Draw the phasor diagram and use it to obtain the expression for
(i) impedance of the circuit and
(ii) phase angle.
First a set of n equal resistors of R each is connected in series to a battery of emf E and internal resistance R. A current I is observed to flow. Then the n resistors are connected in parallel to the same battery. It is observed that the current becomes 10 times. What is n ?
(a) Define the term ‘conductivity’ of a metallic wire. Write its SI unit.
(b) Using the concept of free electrons in a conductor, derive the expression for the conductivity of a wire in terms of number density and relaxation time. Hence obtain the relation between current density and the applied electric field E.
Two point charges + q and –2q are placed at the vertices ‘B’ and ‘C’ of an equilateral triangle ABC of side ‘a‘ as given in the figure. Obtain the expression for (i) the magnitude and (ii) the direction of the resultant electric field at the vertex A due to these two charges.
A sinusoidal voltage of peak value 10 V is applied to a series LCR circuit in which resistance,capacitance and inductance have values of 10 Ω,1 µF and 1 H respectively. Find
(i) the peak voltage across the inductor at resonance
(ii) quality factor of the circuit.
Define the term current density of a metallic conductor. Deduce the relation connecting current density (J) and the conductivity σ of the conductor, when an electric field E, is applied to it.
(i) Three point charges q, – 4q and 2q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side ‘l’ as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the magnitude of the resultant electric force acting on the charge q.
Derive the expression for the current density of a conductor in terms of the conductivity and applied electric field. Explain, with reason how the mobility of electrons in a conductor changes when the potential difference applied is doubled, keeping the temperature of the conductor constant.
