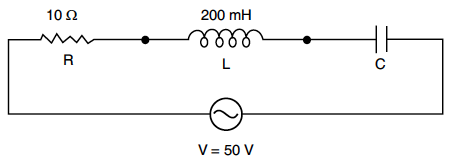
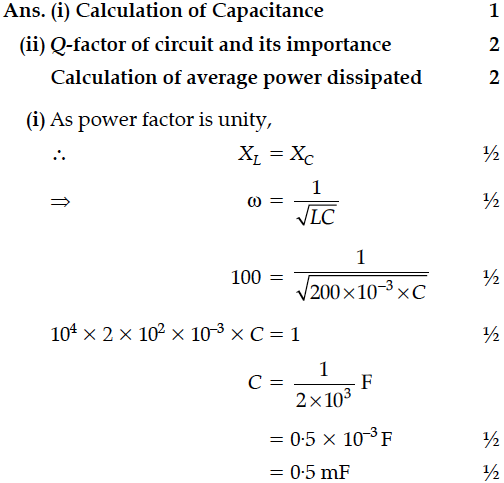
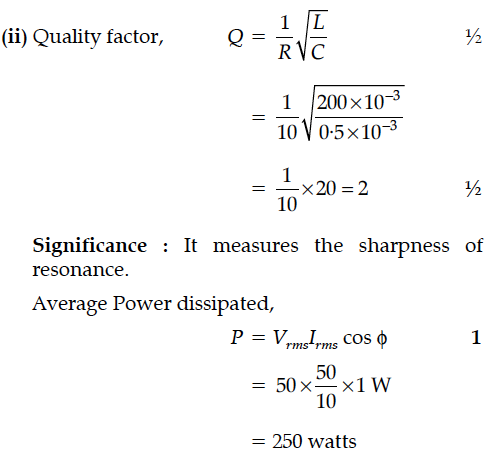
In the following circuit, calculate (i) the capacitance of the capacitor, if the power factor of the circuit is unity, (ii) the Q-factor of this circuit. What is the significance of the Q-factor in ac circuit ? Given the angular frequency of the ac source to be 100rad/s. Calculate the average power dissipated in the circuit.

A circuit containing an 80 mH inductor and a 250 µF capacitor in series connected to a 240 V,100 rad/s supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible.
(i) Obtain rms value of current.
(ii) What is the total average power consumed by the circuit ?
A source of ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
A voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipate over a cycle.Under what conditions is
(i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit,
(ii)maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?
In a series LR circuit = R and power factor of the circuit is P₁. When capacitor with capacitance C such that = is put in series, the power factor becomes P₂. Calculate P₁ / P₂.
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the conditions under which
(i) the impedance of the circuit is minimum, and
(ii) wattless current flows in the circuit.
The figure shows a series LCR circuit connected to a variable frequency of 200 V source with L = 50 mH, C = 80 µF and R = 40 Ω find.
(i) the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance;
(ii) the quality factor (Q) of the circuit.
A sinusoidal voltage of peak value 10 V is applied to a series LCR circuit in which resistance,capacitance and inductance have values of 10 Ω,1 µF and 1 H respectively. Find
(i) the peak voltage across the inductor at resonance
(ii) quality factor of the circuit.
(i) An ac source generating a voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is connected to a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the expression of the current I flowing through it.Plot a graph of V and I versus ωt to show that the current is π/2
ahead of the voltage.
(ii) A resistor of 200Ω and a capacitor of 15 µF are connected in series to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac source.Calculate the current in the circuit and the rms
voltage across the resistor and the capacitor. Why the algebraic sum of these voltages is more than the source voltage ?
Derive an expression for potential due to a dipole for distances large compared to the size of the dipole. How is the potential due to dipole different from that due to single charge ?
A device ‘X’ is connected to an ac source V = The variation of voltage, current and power in one cycle is shown in the following graph :
In the following circuit, calculate (i) the capacitance of the capacitor, if the power factor of the circuit is unity, (ii) the Q-factor of this circuit. What is the significance of the Q-factor in ac circuit ? Given the angular frequency of the ac source to be 100rad/s. Calculate the average power dissipated in the circuit.
A device X is connected across an ac source of voltage V = V₀ sin ωt. The current through X is given as I = I₀sin(ωt +π/2).
(a) Identify the device X and write the expression for its reactance.
(b) Draw graphs showing variation of voltage and current with time over one cycle of ac, for X.
(c) How does the reactance of the device X vary with frequency of the ac ? Show this variation graphically.
(d) Draw the phasor diagram for the device X.
(i) Obtain the expression for the potential to show due to a point charge.
(ii) Potential, due to an electric dipole (length 2a) varies as the ‘inverse square’ of the distance of the ‘field point’ from the centre of the dipole for r > a.
An ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is applied to a pure inductor L. Obtain an expression for the current in the circuit. Prove that the average power supplied to an inductor over one complete cycle is zero.
