(i) Derive the expression for electric field at a point on the equatorial line of an electric dipole.
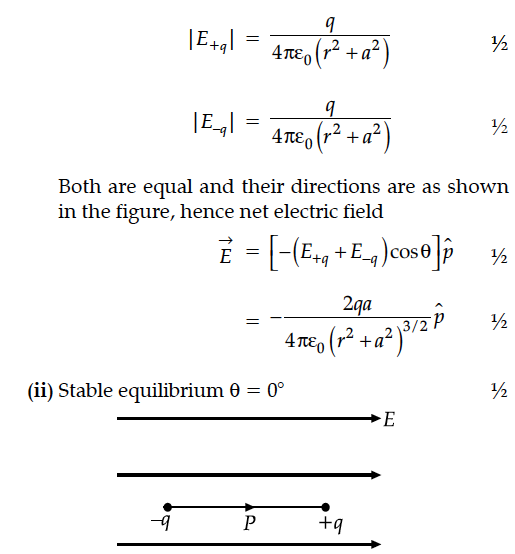
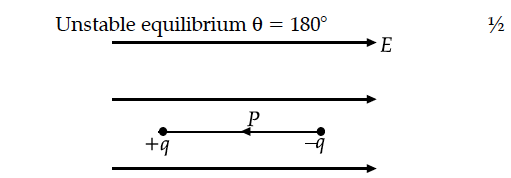
(ii) Depict the orientation of the dipole in (i) stable, (ii) unstable equilibrium in a uniform electric field.
(ii) Depict the orientation of the dipole in (i) stable, (ii) unstable equilibrium in a uniform electric field.
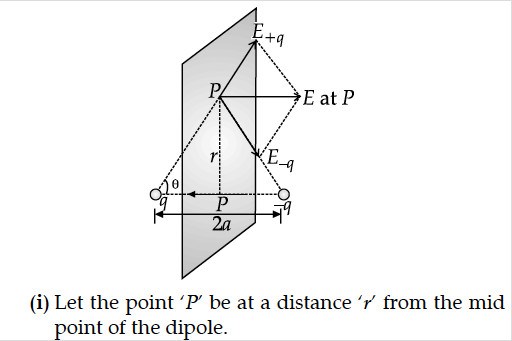
Derive an expression for electric field of a dipole at a point on the equatorial plane of the dipole. How does the field vary at large distances?
Find the expression for electric field intensity in an axial position due to electric dipole.
In the figure the net electric flux through the area... when the system is in air. On immersing the system in water,the net electric flux through the area
An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field.
(i) Show that no translatory force acts on it.
(ii) Derive an expression for the torque acting on it.
(iii) Find work done in rotating the dipole through 180°.
A point charge +Q is placed in the vicinity of a conducting surface. Draw the electric field lines between the surface and the charge.
An electric dipole is held in a uniform electric field.
(i) Show that the net force acting on it is zero.
(ii) The dipole is aligned parallel to the field. Find the work done in rotating it through the angle of 180°.
Three charges each equal to 2 μC are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle. If force between any two charges is 2F, then the net force on either will be:
An inductor L of inductance is connected in series with a bulb B and an ac source. How would brightness of the bulb change when
(i) number of turns in the inductor is reduced,
(ii) an iron rod is inserted in the inductor and
(iii) a capacitor of reactance is inserted in series in the circuit. Justify your answer in each case.
(i) When an ac source is connected to an ideal inductor shows that the average power supplied by the source over a complete cycle is zero.
(ii) A lamp is connected in series with an inductor and an ac source. What happens to the brightness of the lamp when the key is plugged in and an iron rod is inserted inside the inductor ? Explain.
A particle, having a charge +5 µC, is initially at rest at the point x = 30 cm on the x-axis. The particle begins to move due to the presence of a charge Q that is kept fixed at the origin. Find the kinetic energy of the particle at the instant it has moved 15 cm from its initial position if
(a) Q = +15 µC and
(b) Q = – 15 µC
Two cells of emfs E₁ & E₂ and internal resistances r₁ & r₂ respectively are connected in parallel. Obtain expressions for the equivalent.
(i) resistance and
(ii) emf of the combination
(i) The potential difference applied across a given resistor is altered so that the heat produced per second increases by a factor of 9. By what factor does the applied potential difference change ?
(ii) In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 W are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 W. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
(i) A point charge (+Q) is kept in the vicinity of an uncharged conducting plate. Sketch electric field lines between the charge and the plate.
(ii) Two infinitely large plane thin parallel sheets having surface charge densities σ₁ and σ₂ (σ₁ > σ₂) are shown in the figure. Write the magnitudes and directions of the fields in the regions marked II and III.
Show that in the free oscillations of an LC circuit, the sum of energies stored in the capacitor and the inductor is constant in time.
