(i) Prove that current flowing through an ideal inductor connected across ac source, lags the voltage in phase by .
(ii) An inductor of self inductance 100 mH, and a bulb are connected in series with ac source of rms voltage 10V, 50 Hz. It is found that effective voltage of the circuit leads the current in phase by .Calculate the inductance of the inductor used and average power dissipated in the circuit, if a current of 1 A flows in the circuit.
(ii) An inductor of self inductance 100 mH, and a bulb are connected in series with ac source of rms voltage 10V, 50 Hz. It is found that effective voltage of the circuit leads the current in phase by .Calculate the inductance of the inductor used and average power dissipated in the circuit, if a current of 1 A flows in the circuit.
(i) When an ac source is connected to an ideal inductor shows that the average power supplied by the source over a complete cycle is zero.
(ii) A lamp is connected in series with an inductor and an ac source. What happens to the brightness of the lamp when the key is plugged in and an iron rod is inserted inside the inductor ? Explain.
A source of ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
(i) Find the value of the phase difference between the current and the voltage in the series LCR circuit shown below. Which one leads in phase : current or voltage ?
(ii) Without making any other change, find the value of the additional capacitor C₁, to be connected in parallel with the capacitor C, in order to make the power factor of the circuit unity.
An inductor of 200 mH, capacitor of 400 µF and a resistor of 10 Ω are connected in series to ac source of 50 V of variable frequency. Calculate the
(a) angular frequency at which maximum power dissipation occurs in the circuit and the corresponding value of the effective current, and
(b) value of Q-factor in the circuit.
(i) When an ac source is connected to an ideal capacitor show that the average power supplied by the source over a complete cycle is zero.
(ii) A lamp is connected in series with a capacitor.Predict your observation when the system is connected first across a dc and then an ac source.What happens in each case if the capacitance of the capacitor is reduced ?
In the following circuit, calculate (i) the capacitance of the capacitor, if the power factor of the circuit is unity, (ii) the Q-factor of this circuit. What is the significance of the Q-factor in ac circuit ? Given the angular frequency of the ac source to be 100rad/s. Calculate the average power dissipated in the circuit.
A circuit containing an 80 mH inductor and a 250 µF capacitor in series connected to a 240 V,100 rad/s supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible.
(i) Obtain rms value of current.
(ii) What is the total average power consumed by the circuit ?
Derive an expression for potential due to a dipole for distances large compared to the size of the dipole. How is the potential due to dipole different from that due to single charge ?
(i) An ac source generating a voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is connected to a capacitor of capacitance C. Find the expression of the current I flowing through it.Plot a graph of V and I versus ωt to show that the current is π/2
ahead of the voltage.
(ii) A resistor of 200Ω and a capacitor of 15 µF are connected in series to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac source.Calculate the current in the circuit and the rms
voltage across the resistor and the capacitor. Why the algebraic sum of these voltages is more than the source voltage ?
Two point charges q and –q are located at points (0, 0, – a) and (0, 0, a) respectively.
(i) Find the electrostatic potential at (0, 0, z) and (x, y, 0).
(ii) How much work is done in moving a small test charge from the point (5,0,0) to (– 7, 0, 0) along the x-axis ?
(iii) How would your answer change if the path of the test charge between the same points is not along the x-axis but along any other random path ?
(iv) If the above point charges are now placed in the same positions in the uniform external electric field what would be the potential energy of the charge system in its orientation of unstable equilibrium ?
Justify your answer in each case.
A device ‘X’ is connected to an ac source V = The variation of voltage, current and power in one cycle is shown in the following graph :
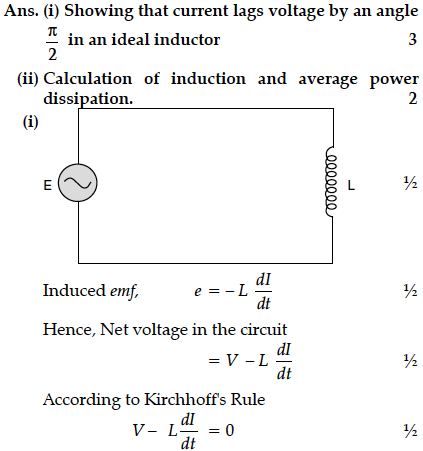
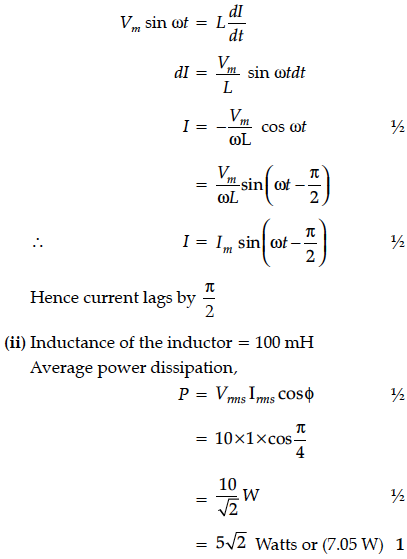
(i) Prove that current flowing through an ideal inductor connected across ac source, lags the voltage in phase by .
(ii) An inductor of self inductance 100 mH, and a bulb are connected in series with ac source of rms voltage 10V, 50 Hz. It is found that effective voltage of the circuit leads the current in phase by .Calculate the inductance of the inductor used and average power dissipated in the circuit, if a current of 1 A flows in the circuit.
In the following circuit, calculate (i) the capacitance of the capacitor, if the power factor of the circuit is unity, (ii) the Q-factor of this circuit. What is the significance of the Q-factor in ac circuit ? Given the angular frequency of the ac source to be 100rad/s. Calculate the average power dissipated in the circuit.
(i) Why do the 'free electrons', in a metal wire, 'flowing by themselves', not cause any current flow in the wire ?
Define 'drift velocity' and obtain an expression for the current flowing in a wire, in terms of the 'drift velocity' of the free electrons.
(ii) Use the above expression to show that the 'resistivity', of the material of a wire, is inversely proportional to the 'relaxation time' for the 'free electrons' in the metal.
