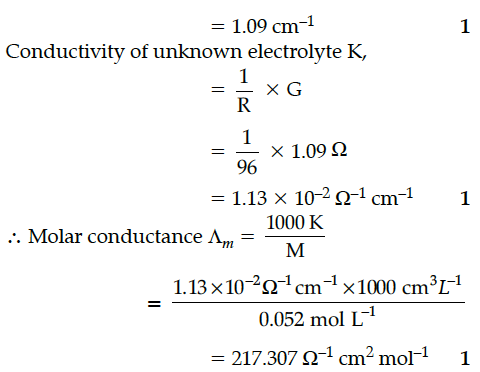
When a certain conductance cell was filled with 0.1 M KCl, it has a resistance of 85 ohm at 25°C. When the same cell was filled with an aqueous solution of 0.052 M unknown electrolyte, the resistance was 96 ohms. Calculate the molar conductance of the electrolyte at this concentration.
[Specific conductance of 0.1 M KCl = 1.29 × 10⁻² ohm⁻¹ cm⁻¹]
[Specific conductance of 0.1 M KCl = 1.29 × 10⁻² ohm⁻¹ cm⁻¹]
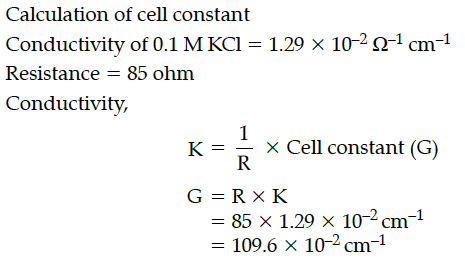
Following reactions can occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous silver nitrate solution using Pt electrodes:
(i) State the law which helps to determine the limiting molar conductivity of weak electrolyte.
(ii) Calculate limiting molar conductivity of CaSO₄ (limiting molar conductivity of calcium and sulphate ions are 119.0 and 160.0 Scm² mol⁻¹ respectively)
Looking at the setup of an electrochemical cell, what happens when \(E_{ext}\) > 1.1 V
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M KOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 45.5 cm is 4.55 × 10³ ohm. Calculate its molar conductivity.
The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called ___________.
a. Cell potential.
b. Electromotive Force.
c. Potential difference.
d. Cell voltage.
The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L⁻¹ methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm² mol⁻¹. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given λ°(H⁺) = 349.6 S cm² mol⁻¹ and λ°(HCOO⁻) = 54.6 S cm² mol⁻¹.
The conductivity of a 0.01 M solution of acetic acid at 298 K is 1.65 x 10⁻⁴ S cm⁻¹. Calculate molar conductivity () of the solution.
Calculate the molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Conductivity of 2.5 × 10⁻⁴M methanoic acid is 5.25 × 10⁻⁵ Scm⁻¹.
Given : = 50.5Scm² mol⁻¹
The magnetic moment of few transition metal ions
are given below:
The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L⁻¹ methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm² mol⁻¹. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given λ°(H⁺) = 349.6 S cm² mol⁻¹ and λ°(HCOO⁻) = 54.6 S cm² mol⁻¹.
(i) Complete the following equations :
(a) 2MnO₄⁻ + 5SO₃²⁻ + 6H⁺ →
(b) Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 6Fe²⁺ + 14H⁺ →
(ii) Based on the data, arrange Fe²⁺, Mn²⁺ and Cr²⁺ in the increasing order of stability of +2 oxidation state.
E°(Cr³⁺/Cr²⁺) = -0.4 V
E°(Mn³⁺/Mn²⁺) = +1.5 V
E°(Fe³⁺/Fe²⁺) = + 0.8 V
When a certain conductance cell was filled with 0.1 M KCl, it has a resistance of 85 ohm at 25°C. When the same cell was filled with an aqueous solution of 0.052 M unknown electrolyte, the resistance was 96 ohms. Calculate the molar conductance of the electrolyte at this concentration.
[Specific conductance of 0.1 M KCl = 1.29 × 10⁻² ohm⁻¹ cm⁻¹]
Give reasons :
(i) Mn shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine it shows the highest oxidation state of +4.
(ii) Transition metals show variable oxidation states.
(iii) Actinoids show irregularities in their electronic configurations.
(i) Give reasons for the following :
(a) Compounds of transition elements are generally coloured.
(b) MnO is basic while Mn₂O₇ is acidic.
(ii) Calculate the magnetic moment of a divalent ion in aqueous medium if its atomic number is 26.
