The magnetic moment of few transition metal ions
are given below:
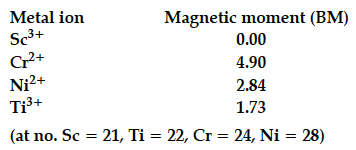
Which of the given metal ions:
(i) has the maximum number of unpaired electrons?
(ii) force colourless aqueous solution?
(iii) exhibits the most stable +3 oxidation state?
are given below:
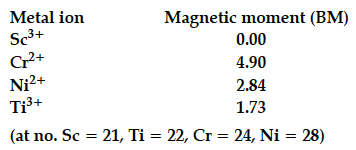
Which of the given metal ions:
(i) has the maximum number of unpaired electrons?
(ii) force colourless aqueous solution?
(iii) exhibits the most stable +3 oxidation state?
(i) Cr²⁺
(ii) Sc³⁺
(iii) Sc³⁺
(ii) Sc³⁺
(iii) Sc³⁺
Metallic radii of some transition elements are given below. Which of these elements will have highest density?
Suggest reasons for the following features of transition metal chemistry :
(i) The transition metals and their compounds are usually paramagnetic.
(ii) The transition metals exhibit variable oxidation states.
Explain the following observation :
Most of the transition metal ions exhibit characteristic colour in aqueous solution.
The magnetic moment is associated with its spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. Spin only magnetic moment value of Cr³⁺ ion is
(a) 2.87 BM
(b) 3.87 BM
(c) 3.47 BM
(d) 3.57 BM
Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equations for its reaction with (i) an iodide (ii) H₂S.
Explain the following :
(i) The enthalpies of atomization of transition metals are quite high.
(ii) The transition metals and many of their compounds act as good catalysts.
Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidified permanganate solution react with oxalic acid ?
Write the ionic equations for the reactions.
Consider the standard electrode potential values (M²⁺/M) of the elements of the first transition series.
Calculate emf of the following cell
Cd/\(Cd^{2+}\) (.10 M)//\(H_+\) (.20 M)/\(H_2\) (0.5 atm)/Pt
[Given E° for \(Cd^{2+}\) /Cd = -0.403V]
The magnetic moment of few transition metal ions
are given below:
Out of the following pairs, predict with reason which pair will allow greater conduction of electricity:
(i) Silver wire at 30°C or silver wire at 60°C.
(ii) 0.1 M \(CH_3\)COOH solution or 1 M \(CH_3\)COOH solution.
(iii) KCl solution at 20°C or KCl solution at 50°C.
Consider the reaction: Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 14H⁺ + 6e⁻ -> 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O. What is the quantity of electricity in coulombs needed to reduce 1 mol of Cr₂O₇²⁻?
Complete the following reactions—
(i) Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 6Fe²⁺ + 14H⁺ →
(ii) 2CrO₄²⁻ + 2H⁺ →
(iii) 2MnO₄⁻ + 5C₂O₄²⁻ + 16H⁺ →
Calculate the molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Conductivity of 2.5 × 10⁻⁴M methanoic acid is 5.25 × 10⁻⁵ Scm⁻¹.
Given : = 50.5Scm² mol⁻¹
