(i) Give reasons for the following :
(a) Compounds of transition elements are generally coloured.
(b) MnO is basic while Mn₂O₇ is acidic.
(ii) Calculate the magnetic moment of a divalent ion in aqueous medium if its atomic number is 26.
(a) Compounds of transition elements are generally coloured.
(b) MnO is basic while Mn₂O₇ is acidic.
(ii) Calculate the magnetic moment of a divalent ion in aqueous medium if its atomic number is 26.
(i) (a) Due to d-d transition.
(b) Due to higher oxidation state of Mn₂O₇/ Due to high polarizing power of Mn(VII).
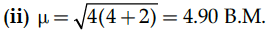
(b) Due to higher oxidation state of Mn₂O₇/ Due to high polarizing power of Mn(VII).
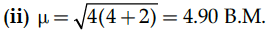
Suggest reasons for the following features of transition metal chemistry :
(i) The transition metals and their compounds are usually paramagnetic.
(ii) The transition metals exhibit variable oxidation states.
(i) Account for the following :
(a) Cu⁺ is unstable in an aqueous solution.
(b) Transition metals form complex compounds.
(ii) Complete the following equation :
CrO₂₇²⁻ + 8H⁺ + 3NO₂⁻ →
Explain the following :
(i) The enthalpies of atomization of transition metals are quite high.
(ii) The transition metals and many of their compounds act as good catalysts.
Account for the following :
(i) CuCl₂ is more stable than Cu₂Cl₂.
(ii) Atomic radii of 4d and 5d series elements are nearly same.
(iii) Hydrochloric acid is not used in permanganate titration.
Write the formula of an oxo-anion of Manganese (Mn) in which it shows the oxidation state equal to its group number.
Explain the following observation :
Most of the transition metal ions exhibit characteristic colour in aqueous solution.
How would you account for the following ? Many of the transition elements are known to form interstitial compounds.
(i) Give reasons for the following :
(a) Compounds of transition elements are generally coloured.
(b) MnO is basic while Mn₂O₇ is acidic.
(ii) Calculate the magnetic moment of a divalent ion in aqueous medium if its atomic number is 26.
Calculate emf of the following cell
Cd/\(Cd^{2+}\) (.10 M)//\(H_+\) (.20 M)/\(H_2\) (0.5 atm)/Pt
[Given E° for \(Cd^{2+}\) /Cd = -0.403V]
Write the preparation of following :
(i) KMnO₄ from K₂MnO₄
(ii) Na₂CrO₄ from FeCr₂O₄
(iii) Cr₂O₇²⁻ from CrO₄²⁻
Account for the following :
(i) CuCl₂ is more stable than Cu₂Cl₂.
(ii) Atomic radii of 4d and 5d series elements are nearly same.
(iii) Hydrochloric acid is not used in permanganate titration.
The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L⁻¹ methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm² mol⁻¹. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given λ°(H⁺) = 349.6 S cm² mol⁻¹ and λ°(HCOO⁻) = 54.6 S cm² mol⁻¹.
(a) Calculate G° for the reaction
Zn(s) + \(Cu^{2+}\)(aq) → \(Zn^{2+}\)(aq) + Cu(s)
Given: E° for \(Zn^{2+}\)/Zn = -0.76V and E° for \(Cu^{2+}\)/Cu = +0.34 V
R = 8.314 \(JK^{–1}\) \(mol^{–1}\), F = 96500 \(mol^{–1}\)
Consider the standard electrode potential values (M²⁺/M) of the elements of the first transition series.
