(i) State the law which helps to determine the limiting molar conductivity of weak electrolyte.
(ii) Calculate limiting molar conductivity of CaSO₄ (limiting molar conductivity of calcium and sulphate ions are 119.0 and 160.0 Scm² mol⁻¹ respectively)
(ii) Calculate limiting molar conductivity of CaSO₄ (limiting molar conductivity of calcium and sulphate ions are 119.0 and 160.0 Scm² mol⁻¹ respectively)
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions :
(i) The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contribution of the anions and cations of the electrolyte.
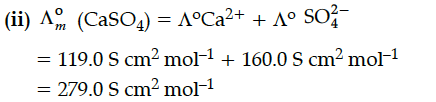
(i) The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contribution of the anions and cations of the electrolyte.
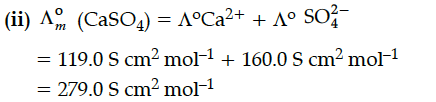
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution ?
The conductivity of a 0.01 M solution of acetic acid at 298 K is 1.65 x 10⁻⁴ S cm⁻¹. Calculate molar conductivity () of the solution.
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M KOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 45.5 cm is 4.55 × 10³ ohm. Calculate its molar conductivity.
The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L⁻¹ methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm² mol⁻¹. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given λ°(H⁺) = 349.6 S cm² mol⁻¹ and λ°(HCOO⁻) = 54.6 S cm² mol⁻¹.
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 Scm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity.
The conductivity of metals decreases while that of electrolytes increases with increase in temperature. Why?
(i) Following reactions occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous silver chloride solution :
= +0.80 V
= 0.00 V
On the basis of their standard reduction electrode potential (E°) values, which reaction is feasible at the cathode and why ?
(ii) Define limiting molar conductivity. Why conductivity of an electrolyte solution decreases with the decrease in concentration ?
Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equations for its reaction with (i) an iodide (ii) H₂S.
State Raoult’s law for a solution containing nonvolatile solute. What type of deviation from Raoult’s law is shown by a solution of chloroform and acetone and why?
What is meant by ‘disproportionation’ ? Give an example of a disproportionation reaction in aqueous solution.
Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidified permanganate solution react with oxalic acid ?
Write the ionic equations for the reactions.
Why a mixture of Carbon disulphide and acetone shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law? What type of azeotrope is formed by this mixture?
