(i) Following reactions occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous silver chloride solution :
= +0.80 V
= 0.00 V
On the basis of their standard reduction electrode potential (E°) values, which reaction is feasible at the cathode and why ?
(ii) Define limiting molar conductivity. Why conductivity of an electrolyte solution decreases with the decrease in concentration ?
= +0.80 V
= 0.00 V
On the basis of their standard reduction electrode potential (E°) values, which reaction is feasible at the cathode and why ?
(ii) Define limiting molar conductivity. Why conductivity of an electrolyte solution decreases with the decrease in concentration ?
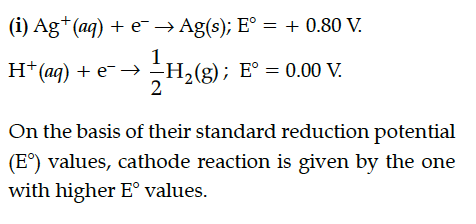

In a galvanic cell, the following cell reactions occurs:
E°cell = +1.56 V
(i) Is the direction of flow of electrons from zinc to silver or silver to zinc?
(ii) How will concentration of Zn²⁺ ions and Ag⁺ ions be affected when the cell functions?
Following reactions can occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous silver nitrate solution using Pt electrodes:
The following curve is obtained when molar conductivity is plotted against the square root of concentration, c½ for two electrolytes A and B :
Assertion : Conductivity of all electrolytes decreases on dilution.
Reason : On dilution number of ions per unit volume decreases.
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but the reason is true.
Assertion: \(E_o\) cell should have a positive value for the cell to function.
Reason: \(E_{cathode}\) < \(E_{anode}\).
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but the reason is true.
Assertion : Λᵒ m for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason : For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but the reason is true.
There are two possible reactions for cathode in the electrolysis of aqueous
\(ZnCl_2\) :\(Zn^{2+}\) (aq) + 2\(e^-\) → Zn(s) \(E^0\) = -0.76 V
2\(H_2\)O (l) + 2\(e^-\) → H2 (g) + 2\(OH^-\) (aq) \(E^0\) = - 0.83 V
Which one will take place? Why?
Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(a) Fe²⁺ + MnO₄⁻ + H⁺ →
(b) MnO₄⁻ + H₂O + I⁻ →
In the following ions:
Mn³⁺, V³⁺, Cr³⁺, Ti⁴⁺
(Atomic no: Mn = 25, V = 23, Cr = 24, Ti = 22)
(a) Which ion is most stable in an aqueous solution?
(b) Which ion is the strongest oxidizing agent?
(c) Which ion is colourless?
(d) Which ion has the highest number of unpaired electrons?
State Henry’s law. What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of a gas in a liquid ?
A 1.00 molar aqueous solution of trichloroacetic acid (CCl₃COOH) is heated to its boiling point. The solution has the boiling point of 100.18 °C. Determine the van’t Hoff factor for trichloroacetic acid. ( for water = 0.512 K kg mol⁻¹).
State Raoult’s law for a solution containing nonvolatile solute. What type of deviation from Raoult’s law is shown by a solution of chloroform and acetone and why?
Define the following terms :
(i) Molar conductivity (),
(ii) Secondary batteries.
