The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L⁻¹ methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm² mol⁻¹. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given λ°(H⁺) = 349.6 S cm² mol⁻¹ and λ°(HCOO⁻) = 54.6 S cm² mol⁻¹.
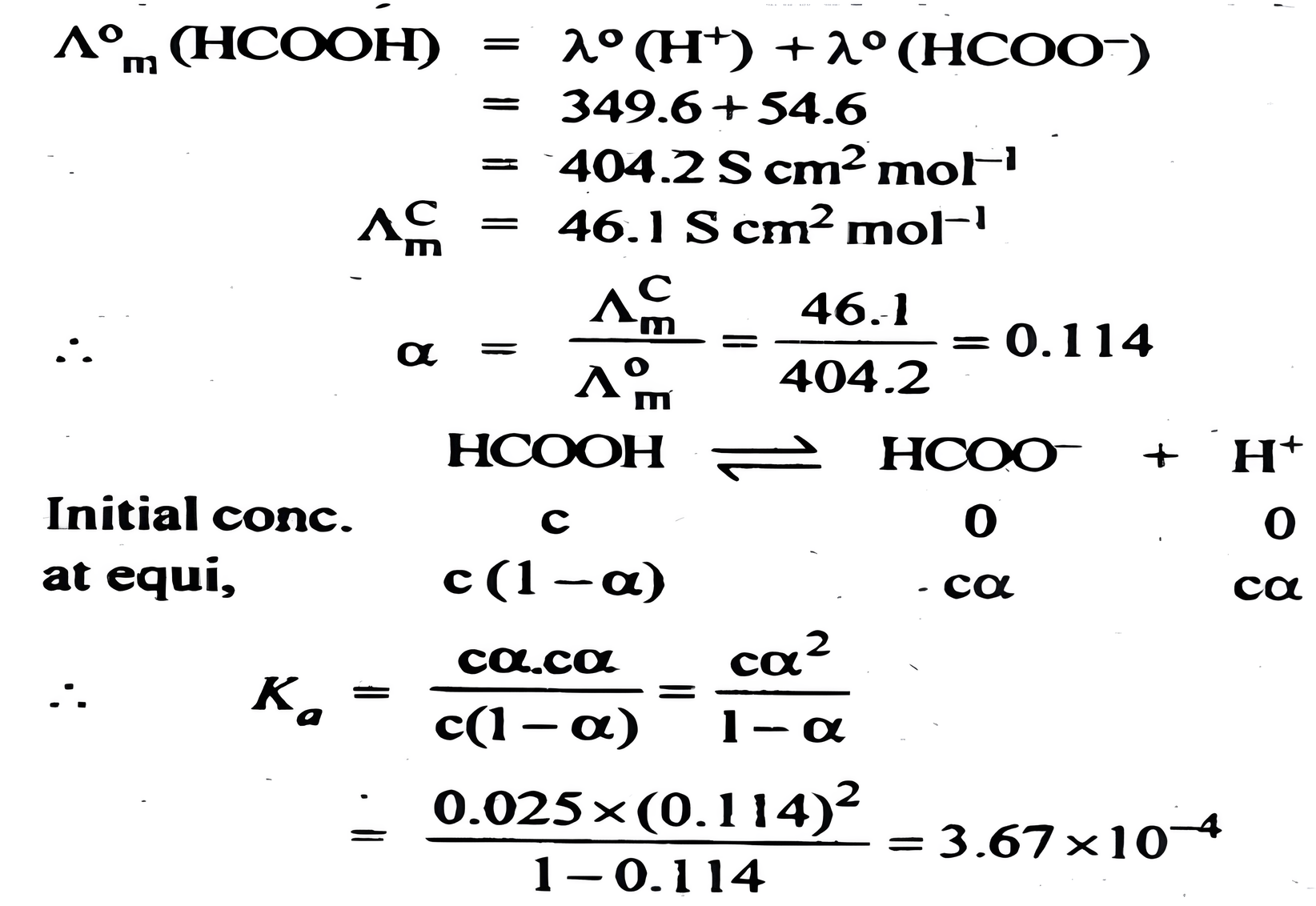
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 Scm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity.
The conductivity of a 0.01 M solution of acetic acid at 298 K is 1.65 x 10⁻⁴ S cm⁻¹. Calculate molar conductivity () of the solution.
The conductivity of an aqueous solution of NaCl in a cell is 92 \(Ω^{−1}\) \(cm^{-1}\) the resistance offered by this cell is 247.8 Ω . Calculate the cell constant.
Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of acetic acid if its molar conductivity () is 39.05 Scm² mol⁻¹. Given (H⁺) = 349.6 Scm² mol⁻¹ and (CH₃COO⁻) = 40.9 Scm² mol⁻¹..
The conductivity of metals decreases while that of electrolytes increases with increase in temperature. Why?
How many electrons flow when a current of 5 amps is passed through a solution for 193 sec ? Given F = 96500 C. \(N_0\) = 6.002 × \(10^{23}\) \(mol^{-1}\).
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M KOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 45.5 cm is 4.55 × 10³ ohm. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Out of the following pairs, predict with reason which pair will allow greater conduction of electricity:
(i) Silver wire at 30°C or silver wire at 60°C.
(ii) 0.1 M \(CH_3\)COOH solution or 1 M \(CH_3\)COOH solution.
(iii) KCl solution at 20°C or KCl solution at 50°C.
Consider the reaction: Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 14H⁺ + 6e⁻ -> 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O. What is the quantity of electricity in coulombs needed to reduce 1 mol of Cr₂O₇²⁻?
Consider the standard electrode potential values (M²⁺/M) of the elements of the first transition series.
(i) Account for the following :
(a) Cu⁺ is unstable in an aqueous solution.
(b) Transition metals form complex compounds.
(ii) Complete the following equation :
CrO₂₇²⁻ + 8H⁺ + 3NO₂⁻ →
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M KOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 45.5 cm is 4.55 × 10³ ohm. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Account for the following :
(i) CuCl₂ is more stable than Cu₂Cl₂.
(ii) Atomic radii of 4d and 5d series elements are nearly same.
(iii) Hydrochloric acid is not used in permanganate titration.
(a) Calculate G° for the reaction
Zn(s) + \(Cu^{2+}\)(aq) → \(Zn^{2+}\)(aq) + Cu(s)
Given: E° for \(Zn^{2+}\)/Zn = -0.76V and E° for \(Cu^{2+}\)/Cu = +0.34 V
R = 8.314 \(JK^{–1}\) \(mol^{–1}\), F = 96500 \(mol^{–1}\)
