The figure shows a plot of terminal voltage ‘V’ versus the current ‘i’ of a given cell. Calculate from the graph
(i) emf of the cell and (ii) internal resistance of the cell.
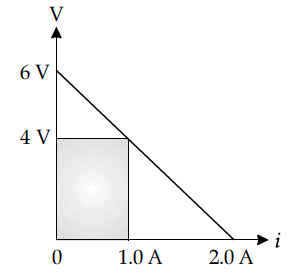
(i) emf of the cell and (ii) internal resistance of the cell.

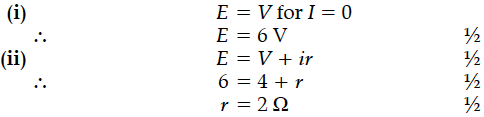
Plot a graph showing the variation of current I versus resistance R, connected to a cell of emf E and internal resistance r.
The plot of the variation of potential difference across a combination of three identical cells in series, versus current is shown below. What is the emf and internal resistance of each cell ?
When electrons drift in a metal from lower to higher potential, does it mean that all the free electrons of the metal are moving in the same direction ?
A 9 V battery is connected in series with a resistor. The terminal voltage is found to be 8 V. Current through the circuit is measured as 5 A. What is the internal resistance of the battery?
A network of resistors is connected to a 16 V battery with internal resistance of 1 Ω, as shown in the following figure. Compute the equivalent resistance of the network.
Using the concept of drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor, deduce the relationship between current density and resistivity of the conductor.
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the total resistance of the circuit and the current in the arm CD.
A small metallic sphere carrying charge +Q is located at the centre of a spherical cavity in a large uncharged metallic spherical shell. Write the charges on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell. Write the expression for the electric field at the point P1.
A 9 V battery is connected in series with a resistor. The terminal voltage is found to be 8 V. Current through the circuit is measured as 5 A. What is the internal resistance of the battery?
An alternating voltage given by V = 140sin314 t is connected across a pure resistor of 50 Find :
(i) the frequency of the source.
(ii) the rms current through the resistor.
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the current through each resistor.
An alternating voltage E = E₀ sin ωt is applied to the circuit containing a resistor R connected in series with a black box. The current in the circuit is found to be I=I₀ (sin ωt+π/4)
Three concentric metallic shells A, B and C of radii a, b and c (a < b < c) have surface charge densities +σ, –σ and +σ respectively as shown in the figure.
A test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure.
