Using the concept of drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor, deduce the relationship between current density and resistivity of the conductor.
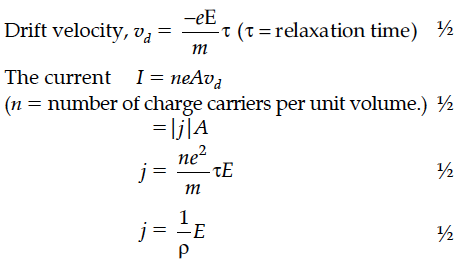
Write the expression for the drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor of length l across which a potential difference V is applied.
How does the random motion of free electrons in a conductor get affected when a potential difference is applied across its ends ?
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the total resistance of the circuit and the current in the arm CD.
In the two electric circuits shown in the figure, determine the readings of ideal ammeter (A) and the ideal voltmeter (V).
A battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to a 4 Ω resistor as shown in the figure.
N spherical droplets, each of radius r, have been charged to have a potential V each. If all these droplets were to coalesce to form a single large drop, what would be the potential of this large drop ?
(It is given that the capacitance of a sphere of radius x equals
A 9 V battery is connected in series with a resistor. The terminal voltage is found to be 8 V. Current through the circuit is measured as 5 A. What is the internal resistance of the battery?
The figure shows a series LCR circuit connected to a variable frequency of 200 V source with L = 50 mH, C = 80 µF and R = 40 Ω find.
(i) the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance;
(ii) the quality factor (Q) of the circuit.
Write two properties of equipotential surfaces. Depict equipotential surfaces due to an isolated point charge. Why do the equipotential surfaces get closer as the distance between the equipotential surfaces and the source charge decreases ?
A test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure.
An electric dipole of length 4 cm, when placed with its axis making an angle of 60° with a uniform electric field, experiences a torque of Nm. Calculate the potential energy of the dipole, if it has charge ± 8 nC.
