An alternating voltage given by V = 140sin314 t is connected across a pure resistor of 50 Find :
(i) the frequency of the source.
(ii) the rms current through the resistor.
(i) the frequency of the source.
(ii) the rms current through the resistor.
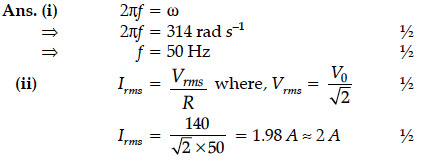
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the conditions under which
(i) the impedance of the circuit is minimum, and
(ii) wattless current flows in the circuit.
State which of the two a capacitor or an inductor, tends to become SHORT when the frequency of the applied alternating voltage has a high value.
In highly inductive load circuit, it is more dangerous when
(a) we close the switch
(b) open the switch
(c) increasing the resistance
(d) decreasing the resistance
Show that in the free oscillations of an LC circuit, the sum of energies stored in the capacitor and the inductor is constant in time.
Obtain the expression for the energy density of magnitude field B produced in the inductor.
In electric arc furnace Cu or Iron is melted due to variation of
(a) current
(b) magnetic field
(c) voltage
(d) electric field
A source of ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected to two external resistances R₁ and R₂ and a perfect ammeter. The current in the circuit is measured in four different situations :
(i) without any external resistance in the circuit
(ii) with resistance R1 only
(iii) with R1 and R2 in series combination
(iv) with R1 and R2 in parallel combination.
The currents measured in the four cases are 0.42 A, 1.05 A, 1.4 A and 4.2 A, but not necessarily in that order. Identify the currents corresponding to the four cases mentioned above.
Two point charges q1 and q2 are located at points (a, 0, 0) and (0, b, 0) respectively. Find the electric field due to both these charges at the point (0, 0, c).
Two cells of emf and have internal resistance and . Deduce an expression for equivalent emf of their parallel combination.
Two metallic wires P₁ and P₂ of the same material and same length but different cross-sectional areas A₁ and A₂ are joined together and then connected to a source of emf. Find the ratio of the drift velocities of free electrons in the wires P₁ and P₂ if the wires are connected
(i) in series, and (ii) in parallel.
Draw a plot showing the variation of resistivity of a (i) conductor and (ii) semiconductor, with the increase in temperature. How does one explain this behaviour in terms of number density of charge carriers and the relaxation time ?
Calculate the amount of work done to dissociate a system of three charges 1 mC, 1 mC and – 4 mC placed on the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 10 cm.
The figure shows two sinusoidal curves representing oscillating supply voltage and current in an ac circuit.
