(i) Account for the following :
(a) Cu⁺ is unstable in an aqueous solution.
(b) Transition metals form complex compounds.
(ii) Complete the following equation :
CrO₂₇²⁻ + 8H⁺ + 3NO₂⁻ →
(a) Cu⁺ is unstable in an aqueous solution.
(b) Transition metals form complex compounds.
(ii) Complete the following equation :
CrO₂₇²⁻ + 8H⁺ + 3NO₂⁻ →
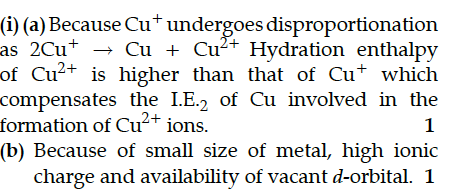
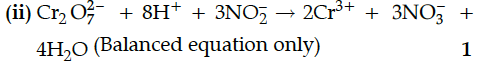
Explain the following :
(i) The enthalpies of atomization of transition metals are quite high.
(ii) The transition metals and many of their compounds act as good catalysts.
Explain the following observation :
Most of the transition metal ions exhibit characteristic colour in aqueous solution.
Account for the following :
(i) CuCl₂ is more stable than Cu₂Cl₂.
(ii) Atomic radii of 4d and 5d series elements are nearly same.
(iii) Hydrochloric acid is not used in permanganate titration.
Suggest reasons for the following features of transition metal chemistry :
(i) The transition metals and their compounds are usually paramagnetic.
(ii) The transition metals exhibit variable oxidation states.
Complete the following chemical equations :
(i) MnO₄⁻(aq) + S₂O₃²⁻(aq) + H₂O(l) →
(ii) Cr₂O₇²⁻(aq) + Fe²⁺(aq) + H⁺(aq) →
Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(a) Fe²⁺ + MnO₄⁻ + H⁺ →
(b) MnO₄⁻ + H₂O + I⁻ →
How would you account for the following ? Many of the transition elements are known to form interstitial compounds.
Calculate the molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Conductivity of 2.5 × 10⁻⁴M methanoic acid is 5.25 × 10⁻⁵ Scm⁻¹.
Given : = 50.5Scm² mol⁻¹
Write the preparation of following :
(i) KMnO₄ from K₂MnO₄
(ii) Na₂CrO₄ from FeCr₂O₄
(iii) Cr₂O₇²⁻ from CrO₄²⁻
Consider the standard electrode potential values (M²⁺/M) of the elements of the first transition series.
Out of the following pairs, predict with reason which pair will allow greater conduction of electricity:
(i) Silver wire at 30°C or silver wire at 60°C.
(ii) 0.1 M \(CH_3\)COOH solution or 1 M \(CH_3\)COOH solution.
(iii) KCl solution at 20°C or KCl solution at 50°C.
Calculate emf of the following cell
Cd/\(Cd^{2+}\) (.10 M)//\(H_+\) (.20 M)/\(H_2\) (0.5 atm)/Pt
[Given E° for \(Cd^{2+}\) /Cd = -0.403V]
The magnetic moment of few transition metal ions
are given below:
(i) Complete the following equations :
(a) 2MnO₄⁻ + 5SO₃²⁻ + 6H⁺ →
(b) Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 6Fe²⁺ + 14H⁺ →
(ii) Based on the data, arrange Fe²⁺, Mn²⁺ and Cr²⁺ in the increasing order of stability of +2 oxidation state.
E°(Cr³⁺/Cr²⁺) = -0.4 V
E°(Mn³⁺/Mn²⁺) = +1.5 V
E°(Fe³⁺/Fe²⁺) = + 0.8 V
