Consider the standard electrode potential values (M²⁺/M) of the elements of the first transition series.
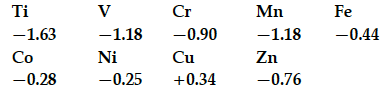
Explain :
(i) E° value for copper is positive.
(ii) E° value of Mn is more negative as expected from the trend.
(iii) Cr³⁺ is a stronger reducing agent than Fe²⁺.
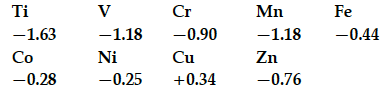
Explain :
(i) E° value for copper is positive.
(ii) E° value of Mn is more negative as expected from the trend.
(iii) Cr³⁺ is a stronger reducing agent than Fe²⁺.
Explain the following observations:
(i) Copper atom has completely filled d orbitals (3d¹⁰) in its ground state, yet it is regarded as a transition element.
(ii) Cr²⁺ is a stronger reducing agent than Fe²⁺ in aqueous solution.
Explain the following :
(i) The enthalpies of atomization of transition metals are quite high.
(ii) The transition metals and many of their compounds act as good catalysts.
(i) Give reasons for the following :
(a) Compounds of transition elements are generally coloured.
(b) MnO is basic while Mn₂O₇ is acidic.
(ii) Calculate the magnetic moment of a divalent ion in aqueous medium if its atomic number is 26.
Suggest reasons for the following features of transition metal chemistry :
(i) The transition metals and their compounds are usually paramagnetic.
(ii) The transition metals exhibit variable oxidation states.
(i) Account for the following :
(a) Cu⁺ is unstable in an aqueous solution.
(b) Transition metals form complex compounds.
(ii) Complete the following equation :
CrO₂₇²⁻ + 8H⁺ + 3NO₂⁻ →
Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidified permanganate solution react with oxalic acid ?
Write the ionic equations for the reactions.
Account for the following :
(i) CuCl₂ is more stable than Cu₂Cl₂.
(ii) Atomic radii of 4d and 5d series elements are nearly same.
(iii) Hydrochloric acid is not used in permanganate titration.
Give reasons :
(i) Mn shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine it shows the highest oxidation state of +4.
(ii) Transition metals show variable oxidation states.
(iii) Actinoids show irregularities in their electronic configurations.
(a) Calculate G° for the reaction
Zn(s) + \(Cu^{2+}\)(aq) → \(Zn^{2+}\)(aq) + Cu(s)
Given: E° for \(Zn^{2+}\)/Zn = -0.76V and E° for \(Cu^{2+}\)/Cu = +0.34 V
R = 8.314 \(JK^{–1}\) \(mol^{–1}\), F = 96500 \(mol^{–1}\)
Calculate emf of the following cell
Cd/\(Cd^{2+}\) (.10 M)//\(H_+\) (.20 M)/\(H_2\) (0.5 atm)/Pt
[Given E° for \(Cd^{2+}\) /Cd = -0.403V]
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M KOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 45.5 cm is 4.55 × 10³ ohm. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Consider the standard electrode potential values (M²⁺/M) of the elements of the first transition series.
Consider the reaction: Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 14H⁺ + 6e⁻ -> 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O. What is the quantity of electricity in coulombs needed to reduce 1 mol of Cr₂O₇²⁻?
(i) Complete the following equations :
(a) 2MnO₄⁻ + 5SO₃²⁻ + 6H⁺ →
(b) Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 6Fe²⁺ + 14H⁺ →
(ii) Based on the data, arrange Fe²⁺, Mn²⁺ and Cr²⁺ in the increasing order of stability of +2 oxidation state.
E°(Cr³⁺/Cr²⁺) = -0.4 V
E°(Mn³⁺/Mn²⁺) = +1.5 V
E°(Fe³⁺/Fe²⁺) = + 0.8 V
