Consider the reaction: Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 14H⁺ + 6e⁻ -> 2Cr³⁺ + 7H₂O. What is the quantity of electricity in coulombs needed to reduce 1 mol of Cr₂O₇²⁻?
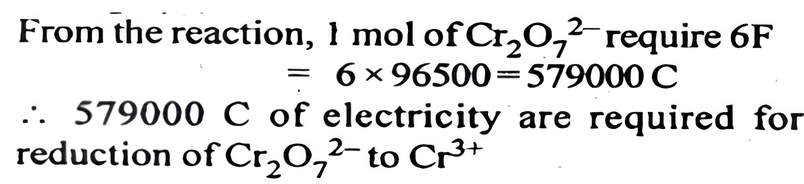
The conductivity of metals decreases while that of electrolytes increases with increase in temperature. Why?
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution ?
Calculate pH of following half-cell. Pt, \(H_2\) / \(H_2\)\(SO_4\) , if its electrode potential is 0.03V.
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 Scm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity.
The potential of a hydrogen electrode at pH = 10 is
a. 0.591 V
b. 0.00 V
c. – 0.591 V
d. -0.059 V
Account for the following :
(i) CuCl₂ is more stable than Cu₂Cl₂.
(ii) Atomic radii of 4d and 5d series elements are nearly same.
(iii) Hydrochloric acid is not used in permanganate titration.
Give reasons :
(i) Mn shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine it shows the highest oxidation state of +4.
(ii) Transition metals show variable oxidation states.
(iii) Actinoids show irregularities in their electronic configurations.
(a) Calculate G° for the reaction
Zn(s) + \(Cu^{2+}\)(aq) → \(Zn^{2+}\)(aq) + Cu(s)
Given: E° for \(Zn^{2+}\)/Zn = -0.76V and E° for \(Cu^{2+}\)/Cu = +0.34 V
R = 8.314 \(JK^{–1}\) \(mol^{–1}\), F = 96500 \(mol^{–1}\)
The vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B at 400 K are 450 and 700 mm Hg respectively. Find out the composition of liquid mixture if total pressure at this temperature is 600 mm Hg.
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M KOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 45.5 cm is 4.55 × 10³ ohm. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Calculate the molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Conductivity of 2.5 × 10⁻⁴M methanoic acid is 5.25 × 10⁻⁵ Scm⁻¹.
Given : = 50.5Scm² mol⁻¹
Calculate emf of the following cell
Cd/\(Cd^{2+}\) (.10 M)//\(H_+\) (.20 M)/\(H_2\) (0.5 atm)/Pt
[Given E° for \(Cd^{2+}\) /Cd = -0.403V]
