Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Standard electrode potentials are used for various processes:
(i) It is used to measure relative strengths of various oxidants and reductants.
(ii) It is used to calculate standard cell potential.
(iii) It is used to predict possible reactions.
A set of half-reactions (in acidic medium) along with their standard reduction potential, E° (in volt) values are given below –
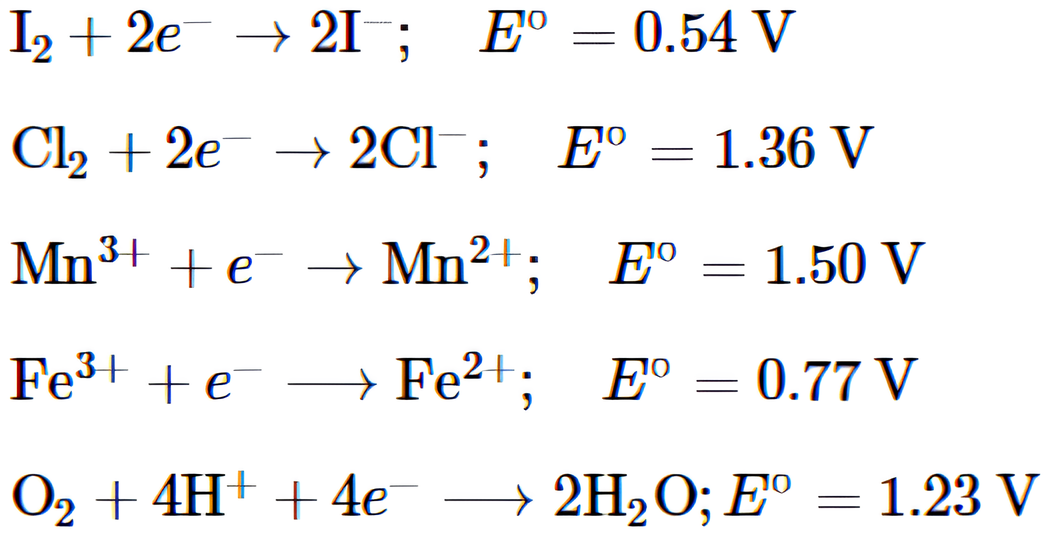
Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) \(CI^-\) is oxidised by \(O_2\).
(b) \(Fe^{2+}\) is oxidised by iodine.
(c) \(I^-\)is oxidised by chlorine.
(d) \(Mn^{2+}\) is oxidised by chlorine.
(ii) \(Mn^{3+}\) is not stable in acidic medium, while \(Fe^{3+}\) is stable because
(a) \(O_2\) oxidises \(Mn^{2+}\) to \(Mn^{3+}\).
(b) \(O_2\) oxidises both \(Mn^{2+}\) to \(Mn^{3+}\) and \(Fe^{2+}\) to \(Fe^{3+}\).
(c) \(Fe^{3-}\) oxidises \(H_2\)O to \(O_2\).
(d) \(Mn^{3+}\) oxidises \(H_2\)O to \(O_2\).
(iii) The strongest reducing agent in the aqueous solution is
(a) \(I^-\).
(b) \(Cl^-\).
(c) \(Mn^{2+}\).
(d) \(Fe^{2+}\).
(iv) The emf for the following reaction is –
\(I_2\) + KCl ⇌ 2KI + \(Cl_2\)
(a) -0.82 V.
(b) +0.82 V.
(c) -0.73 V.
(d) +0.73 V.
(v) The potential of an electrode changes with change in
(a) concentration of ions in solution.
(b) position of electrodes.
(c) voltage of the cell.
(d) all of these.
Standard electrode potentials are used for various processes:
(i) It is used to measure relative strengths of various oxidants and reductants.
(ii) It is used to calculate standard cell potential.
(iii) It is used to predict possible reactions.
A set of half-reactions (in acidic medium) along with their standard reduction potential, E° (in volt) values are given below –
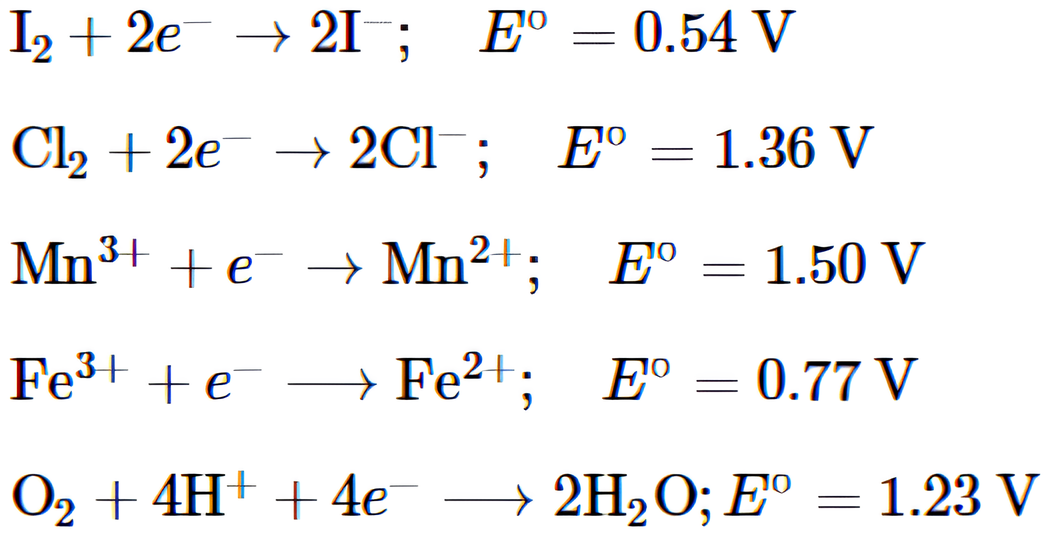
Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) \(CI^-\) is oxidised by \(O_2\).
(b) \(Fe^{2+}\) is oxidised by iodine.
(c) \(I^-\)is oxidised by chlorine.
(d) \(Mn^{2+}\) is oxidised by chlorine.
(ii) \(Mn^{3+}\) is not stable in acidic medium, while \(Fe^{3+}\) is stable because
(a) \(O_2\) oxidises \(Mn^{2+}\) to \(Mn^{3+}\).
(b) \(O_2\) oxidises both \(Mn^{2+}\) to \(Mn^{3+}\) and \(Fe^{2+}\) to \(Fe^{3+}\).
(c) \(Fe^{3-}\) oxidises \(H_2\)O to \(O_2\).
(d) \(Mn^{3+}\) oxidises \(H_2\)O to \(O_2\).
(iii) The strongest reducing agent in the aqueous solution is
(a) \(I^-\).
(b) \(Cl^-\).
(c) \(Mn^{2+}\).
(d) \(Fe^{2+}\).
(iv) The emf for the following reaction is –
\(I_2\) + KCl ⇌ 2KI + \(Cl_2\)
(a) -0.82 V.
(b) +0.82 V.
(c) -0.73 V.
(d) +0.73 V.
(v) The potential of an electrode changes with change in
(a) concentration of ions in solution.
(b) position of electrodes.
(c) voltage of the cell.
(d) all of these.
(i) (d) \(Mn^{2+}\) is oxidised by chlorine.
(ii) c) \(Fe^{3-}\) oxidises \(H_2\)O to \(O_2\).
(iii) (c) \(Mn^{2+}\).
(iv) (a) -0.82 V.
(v) (d) all of these.
(ii) c) \(Fe^{3-}\) oxidises \(H_2\)O to \(O_2\).
(iii) (c) \(Mn^{2+}\).
(iv) (a) -0.82 V.
(v) (d) all of these.
Molar conductivity of solution is the conductance of solution containing one mole of electrolyte, kept between two electrodes having unit length between them and large cross-sectional area, so as to contain the electrolyte. In other words, molar conductivity is the conductance of the electrolytic solution kept between the electrodes of a conductivity cell at unit distance but having area of cross-section large enough to accommodate sufficient volume of solution that contains one mole of the electrolyte. It is denoted by λm.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Assertion : Λᵒ m for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason : For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but the reason is true.
(i) Following reactions occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous silver chloride solution :
= +0.80 V
= 0.00 V
On the basis of their standard reduction electrode potential (E°) values, which reaction is feasible at the cathode and why ?
(ii) Define limiting molar conductivity. Why conductivity of an electrolyte solution decreases with the decrease in concentration ?
Assertion : Conductivity of all electrolytes decreases on dilution.
Reason : On dilution number of ions per unit volume decreases.
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but the reason is true.
Assertion: \(E_o\) cell should have a positive value for the cell to function.
Reason: \(E_{cathode}\) < \(E_{anode}\).
(A) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(C) Assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Assertion is false but the reason is true.
The following curve is obtained when molar conductivity is plotted against the square root of concentration, c½ for two electrolytes A and B :
When a certain conductance cell was filled with 0.1 M KCl, it has a resistance of 85 ohm at 25°C. When the same cell was filled with an aqueous solution of 0.052 M unknown electrolyte, the resistance was 96 ohms. Calculate the molar conductance of the electrolyte at this concentration.
[Specific conductance of 0.1 M KCl = 1.29 × 10⁻² ohm⁻¹ cm⁻¹]
Molar conductivity of solution is the conductance of solution containing one mole of electrolyte, kept between two electrodes having unit length between them and large cross-sectional area, so as to contain the electrolyte. In other words, molar conductivity is the conductance of the electrolytic solution kept between the electrodes of a conductivity cell at unit distance but having area of cross-section large enough to accommodate sufficient volume of solution that contains one mole of the electrolyte. It is denoted by λm.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Standard electrode potentials are used for various processes:
(i) It is used to measure relative strengths of various oxidants and reductants.
(ii) It is used to calculate standard cell potential.
(iii) It is used to predict possible reactions.
A set of half-reactions (in acidic medium) along with their standard reduction potential, E° (in volt) values are given below –
