Show that in the free oscillations of an LC circuit, the sum of energies stored in the capacitor and the inductor is constant in time.
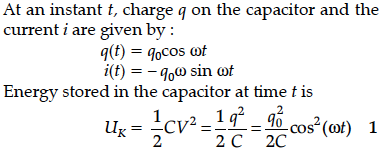
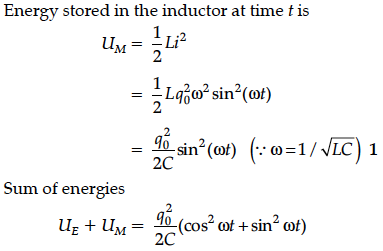
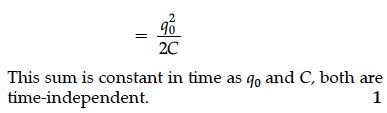
Obtain the expression for the energy density of magnitude field B produced in the inductor.
Show that the current leads the voltage in phase by in an ac circuit containing an ideal capacitor.
State which of the two a capacitor or an inductor, tends to become SHORT when the frequency of the applied alternating voltage has a high value.
In electric arc furnace Cu or Iron is melted due to variation of
(a) current
(b) magnetic field
(c) voltage
(d) electric field
The figure shows a series LCR circuit with L = 5.0 H, C = 80 µF, R = 40 Ω connected to a variable frequency of 240 V source. Calculate
The temperature coefficient of resistivity, for two materials A and B, are 0.0031 / °C and 0.0068 / °C respectively.
Two resistors R1 and R2, made from materials A and B, respectively, have resistances of 200 Ω and 100 Ω at 0°C. Show on a diagram, the 'colour code', of a carbon resistor, that would have a resistance
equal to the series combination of R1 and R2, at a temperature of 100°C.
(Neglect the ring corresponding to the tolerance of the carbon resistor).
A sinusoidal voltage of peak value 10 V is applied to a series LCR circuit in which resistance,capacitance and inductance have values of 10 Ω,1 µF and 1 H respectively. Find
(i) the peak voltage across the inductor at resonance
(ii) quality factor of the circuit.
Obtain the expression for the potential due to an electric dipole of dipole moment p at a point ‘d’ on the axial line.
Two material bars A and B of equal area of crosssection, are connected in series to a DC supply. A is made of usual resistance wire and B of an n-type semiconductor.
(i) In which bar is drift speed of free electrons greater?
(ii) If the same constant current continues to flow for a long time, how will the voltage drop across A and B be affected?
Justify each error.
Define relaxation time of the free electrons drifting in a conductor. How is it related to the drift velocity of free electrons ? Use this relation to deduce the expression for the electrical resistivity of the material.
The following table gives the length of three copper wires, their diameters, and the applied potential difference across their ends. Arrange the wires in increasing order according to the following :
(i) The magnitude of the electric field within them,
(ii) The drift speed of electrons through them, and
(iii) The current density within them.
