(i) An electric dipole is kept first to the left and then to the right of a negatively charged infinite plane sheet having a uniform surface charge density. The arrows p₁ and p₂ show the directions of its electric dipole moments in the two cases.
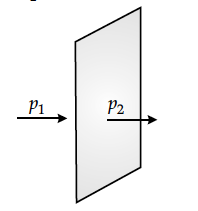
Identify for each case, whether the dipole is in stable or unstable equilibrium. Justify each answer.
(ii) Next, the dipole is kept in a similar way (as shown), near an infinitely long straight wire having uniform negative linear charge density.
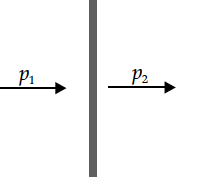
Will the dipole be in equilibrium at these two positions? Justify your answer.

Identify for each case, whether the dipole is in stable or unstable equilibrium. Justify each answer.
(ii) Next, the dipole is kept in a similar way (as shown), near an infinitely long straight wire having uniform negative linear charge density.

Will the dipole be in equilibrium at these two positions? Justify your answer.


An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field with its dipole moment parallel to the field. Find
(i) the work done in turning the dipole till its dipole moment points in the direction opposite to .
(ii) the orientation of the dipole for which the torque acting on it becomes maximum.
Select the correct statements from the following
(i) inside a charged or neutral conductor, electrostatic field is zero.
(ii) the electrostatic field at the surface of the charged conductor must be tangential to the surface at any point.
(iii) there is no net charge at any point inside the conductor.
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) i) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (i), (ii), and (iii)
Which of the following is not a property of electric field lines?
(A) Field lines are closed and continuous curves without any breaks.
(B) Two field lines cannot cross each other.
(C) Field lines start at positive charges and end at negative charges.
(D) They do not form closed loops.
(i) A point charge (+Q) is kept in the vicinity of an uncharged conducting plate. Sketch electric field lines between the charge and the plate.
(ii) Two infinitely large plane thin parallel sheets having surface charge densities σ₁ and σ₂ (σ₁ > σ₂) are shown in the figure. Write the magnitudes and directions of the fields in the regions marked II and III.
Five charges, q each are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side a.
(i) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed ?
(ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by - q ?
An electric dipole is held in a uniform electric field.
(i) Show that the net force acting on it is zero.
(ii) The dipole is aligned parallel to the field. Find the work done in rotating it through the angle of 180°.
The electric flux through a closed gaussian surface depends upon
(A) Permittivity of the medium.
(B) Net charge enclosed only.
(C) Net charge enclosed and permittivity of the medium.
(D) Net charge enclosed, shape and size of the Gaussian surface and permittivity of the medium.
Show that in the free oscillations of an LC circuit, the sum of energies stored in the capacitor and the inductor is constant in time.
(i) Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons.
(ii) How does drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with increase in temperature ? Explain.
(i) An electric dipole is kept first to the left and then to the right of a negatively charged infinite plane sheet having a uniform surface charge density. The arrows p₁ and p₂ show the directions of its electric dipole moments in the two cases.
(i) When an ac source is connected to an ideal capacitor show that the average power supplied by the source over a complete cycle is zero.
(ii) A lamp is connected in series with a capacitor.Predict your observation when the system is connected first across a dc and then an ac source.What happens in each case if the capacitance of the capacitor is reduced ?
Derive an expression for electric field of a dipole at a point on the equatorial plane of the dipole. How does the field vary at large distances?
(i) Derive an expression for drift velocity of electrons in a conductor. Hence deduce Ohm’s law.
(ii) A wire whose cross-sectional area is increasing linearly from its one end to the other, is connected across a battery of V volts. Which of the following quantities remain constant in the wire ?
(a) drift speed
(b) current density
(c) electric current
(d) electric field
Justify your answer.
Two point charges + q and –2q are placed at the vertices ‘B’ and ‘C’ of an equilateral triangle ABC of side ‘a‘ as given in the figure. Obtain the expression for (i) the magnitude and (ii) the direction of the resultant electric field at the vertex A due to these two charges.
