Write the expression for the drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor of length l across which a potential difference V is applied.
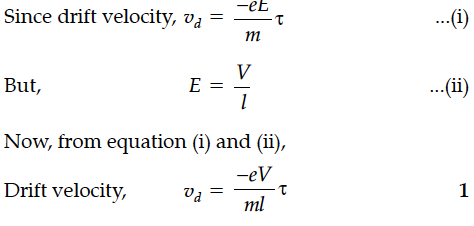
How does the random motion of free electrons in a conductor get affected when a potential difference is applied across its ends ?
Using the concept of drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor, deduce the relationship between current density and resistivity of the conductor.
Give an example of a material each for which temperature coefficient of resistivity is:
(i) positive, (ii) negative.
Plot a graph showing the variation of current I versus resistance R, connected to a cell of emf E and internal resistance r.
A 10 V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a 200 V battery and a resistance of 38Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of the current in the circuit.
Graph showing the variation of current versus voltage for a material GaAs is shown in the figure, identify the region of :
How does the random motion of free electrons in a conductor get affected when a potential difference is applied across its ends ?
Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point ? Give reason.
Two identical cells, each of emf E, having negligible internal resistance, are connected in parallel with each other across an external resistance R. What is the current through this resistance ?
A point charge Q is placed at point ‘O’ as shown in figure. Is the potential at point A, i.e., , greater, smaller or equal to potential, at point B, when Q is (i) positive, and (ii) negative charge?
