Write two properties of equipotential surfaces. Depict equipotential surfaces due to an isolated point charge. Why do the equipotential surfaces get closer as the distance between the equipotential surfaces and the source charge decreases ?
Characteristics of equipotential surfaces :
(i) These surfaces are always perpendicular to field lines.
(ii) No work is done in moving the test charge from one point of equipotential surface to the other.
On reducing the distance of source charge, the electric field becomes strong and equipotential surfaces come closer.
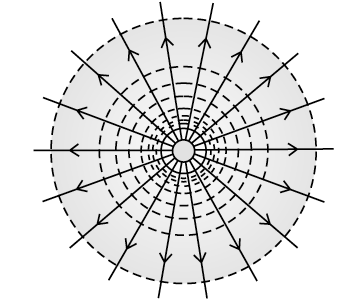
For an isolated point charge, the equipotential surfaces are shown below.
(i) These surfaces are always perpendicular to field lines.
(ii) No work is done in moving the test charge from one point of equipotential surface to the other.
On reducing the distance of source charge, the electric field becomes strong and equipotential surfaces come closer.
For an isolated point charge, the equipotential surfaces are shown below.

(i) Derive the expression for the electric potential due to an electric dipole at a point on its axial line.
(ii) Depict the equipotential surface due to electric dipole.
Derive an expression for potential due to a dipole for distances large compared to the size of the dipole. How is the potential due to dipole different from that due to single charge ?
What is the amount of work done in moving a point charge around a circular arc of radius r at the center where another point charge is located ?
Equipotential surfaces at a great distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are approximately
(a) spheres
(b) planes
(c) paraboloids
(d) ellipsoids
Two point charges q and –2q are kept d distance apart. Find the location of the point relative to charge q at which potential due to this system of charges is zero.
Two capacitors of capacitance 6 µF and 4 µF are put in series across a 120 V battery. What is the potential difference across the 4 µF capacitor?
(a) 72 V
(b) 60 V
(c) 48 V
(d) zero
Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point ? Give reason.
Draw a graph showing variation of resistivity with temperature for nichrome. Which property of nichrome is used to make standard resistance coils ?
Three concentric metallic shells A, B and C of radii a, b and c (a < b < c) have surface charge densities +σ, –σ and +σ respectively as shown in the figure.
Draw a plot showing the variation of (i) electric field (E) and (ii) electric potential (V) with distance r due to a point charge Q.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected to two external resistances R₁ and R₂ and a perfect ammeter. The current in the circuit is measured in four different situations :
(i) without any external resistance in the circuit
(ii) with resistance R1 only
(iii) with R1 and R2 in series combination
(iv) with R1 and R2 in parallel combination.
The currents measured in the four cases are 0.42 A, 1.05 A, 1.4 A and 4.2 A, but not necessarily in that order. Identify the currents corresponding to the four cases mentioned above.
Two point charges q1 and q2 are located at points (a, 0, 0) and (0, b, 0) respectively. Find the electric field due to both these charges at the point (0, 0, c).
Two cells of E.M.F. 10 V and 2 V and internal resistances 10 Ω and 5 Ω respectively, are connected in parallel as shown. Find the effective voltage across R.
A lamp is connected in series with a capacitor. Predict your observation for dc and ac connections. What happens in each if the capacitance of the capacitor is reduced ?
