A torch bulb rated as 4.5 W, 1.5 V is connected as shown in the figure. The emf of the cell needed to make the bulb glow at full intensity is
(a) 4.5 V
(b) 1.5 V
(c) 2.67 V
(d) 13.5 V
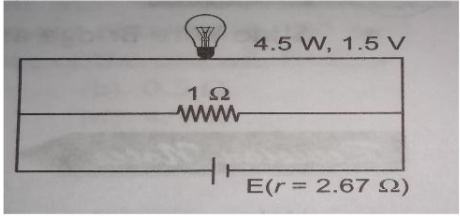
(a) 4.5 V
(b) 1.5 V
(c) 2.67 V
(d) 13.5 V

(d) 13.5 V
Five resistances are combined according to the figure. The equivalent resistances between the points X and Y will be
(a) 10 Ω
(b) 22 Ω
(c) 20 Ω
(d) 50 Ω
In the two electric circuits shown in the figure, determine the readings of ideal ammeter (A) and the ideal voltmeter (V).
The V-i graph for a conductor at temperature T¹ and T² are as shown in the figure. (T² - T¹) is proportional to
(a) cos θ
(b) sin θ
(c) cot 2θ
(d) tan θ
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the total resistance of the circuit and the current in the arm CD.
In meter bridge, the balancing length from left end when standard resistance of 1 Ω is in right gap is found to be 20 cm. The value of unknown resistance is
(a) 0.25 Ω
(b) 0.4 Ω
(c) 0.5 Ω
(d) 4 Ω
A network of resistors is connected to a 16 V battery with internal resistance of 1Ω as shown in the Fig. Compute the equivalent resistance of the network.
(a) 5 ohm
(b) 7 ohm
(c) 9 ohm
(d) 10 ohm
What is the angle between the electric dipole moment and electric field strength due to it on the axial line?
(A) \(0^\circ\)
(B) \(90^\circ\)
(C) \(180^\circ\)
(D) None of these
The distance between two-point charges is increased by 10%. The force of interaction approximately
(A) Increased by 10%
(B) Decrease by 10%
(C) Decrease by 17%
(D) Decrease by 21%
If distance between two current- carrying wires is doubled, then force between them is
(a) halved
(b) doubled
(c) tripled
(d) quadrupled.
A charge q is placed at one corner of the cube. The electric flux passing through any one of its face is
the magnitude of a charge q at the center of two equal and like charges Q so that the three charges are in equilibrium
A. Q
B. Q/2
C. Q/4
D. –Q/4
Unpolarized light is incident on a plane glass surface The angle of incidence so that reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other, them
(a) tan iβ= μ/2
(b) tan iβ = μ
(c) sin iβ = μ
(d) cos iβ = μ
