Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equations for its reaction with (i) an iodide (ii) H₂S.
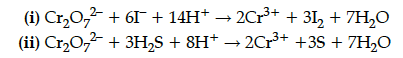
Write the formula of an oxo-anion of Chromium (Cr) in which it shows the oxidation state equal to its group number.
What are the transition elements ? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
Write the formula of an oxo-anion of Manganese (Mn) in which it shows the oxidation state equal to its group number.
Assign the reason for the following :
Copper (I) ion is not known in aqueous solution.
What is meant by ‘disproportionation’ ? Give an example of a disproportionation reaction in aqueous solution.
Explain the following observation :
Most of the transition metal ions exhibit characteristic colour in aqueous solution.
When Cu²⁺ ion is treated with KI, a white precipitate is formed. Explain the reaction with the help of chemical equation.
The conductivity of a 0.01 M solution of acetic acid at 298 K is 1.65 x 10⁻⁴ S cm⁻¹. Calculate molar conductivity () of the solution.
In a galvanic cell, the following cell reactions occurs:
E°cell = +1.56 V
(i) Is the direction of flow of electrons from zinc to silver or silver to zinc?
(ii) How will concentration of Zn²⁺ ions and Ag⁺ ions be affected when the cell functions?
What is meant by positive deviations from Raoult’s law ? Give an example. What is the sign of H for positive deviation ?
State Henry’s law. What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of a gas in a liquid ?
Calculate pH of following half-cell. Pt, \(H_2\) / \(H_2\)\(SO_4\) , if its electrode potential is 0.03V.
(i) State the law which helps to determine the limiting molar conductivity of weak electrolyte.
(ii) Calculate limiting molar conductivity of CaSO₄ (limiting molar conductivity of calcium and sulphate ions are 119.0 and 160.0 Scm² mol⁻¹ respectively)
The conductivity of an aqueous solution of NaCl in a cell is 92 \(Ω^{−1}\) \(cm^{-1}\) the resistance offered by this cell is 247.8 Ω . Calculate the cell constant.
