The conductivity of a 0.01 M solution of acetic acid at 298 K is 1.65 x 10⁻⁴ S cm⁻¹. Calculate molar conductivity () of the solution.
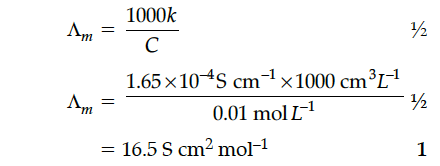
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 Scm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity.
The conductivity of an aqueous solution of NaCl in a cell is 92 \(Ω^{−1}\) \(cm^{-1}\) the resistance offered by this cell is 247.8 Ω . Calculate the cell constant.
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M KOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 45.5 cm is 4.55 × 10³ ohm. Calculate its molar conductivity.
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution ?
The conductivity of metals decreases while that of electrolytes increases with increase in temperature. Why?
What are the transition elements ? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 Scm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(a) Fe²⁺ + MnO₄⁻ + H⁺ →
(b) MnO₄⁻ + H₂O + I⁻ →
The conductivity of an aqueous solution of NaCl in a cell is 92 \(Ω^{−1}\) \(cm^{-1}\) the resistance offered by this cell is 247.8 Ω . Calculate the cell constant.
State Raoult’s law for a solution containing nonvolatile solute. What type of deviation from Raoult’s law is shown by a solution of chloroform and acetone and why?
Define azeotropes. What type of azeotrope is formed by positive deviation from Raoult’s law ?
Give an example.
The conductivity of a 0.01 M solution of acetic acid at 298 K is 1.65 x 10⁻⁴ S cm⁻¹. Calculate molar conductivity () of the solution.
