State Raoult’s law. How is it formulated for solutions of non-volatile solutes ?
Raoult’s law for solution of non-volatile solution :
The relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to the mole fraction of solute when solvent alone is volatile.
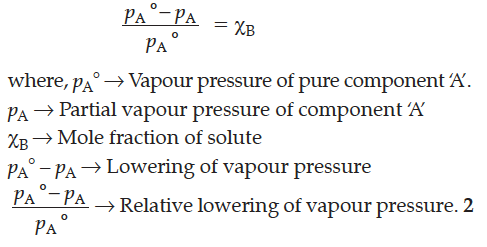
The relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to the mole fraction of solute when solvent alone is volatile.
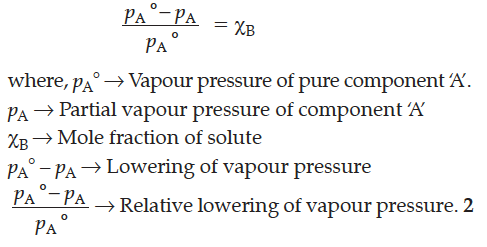
State Henry’s law. What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of a gas in a liquid ?
Explain why :
(i) E° for Mn³⁺/Mn²⁺ couple is more positive than that for Fe³⁺/Fe²⁺. (At. Nos. Mn = 25, Fe = 26).
(ii) Ce³⁺ can be easily oxidized to Ce⁴⁺. (At. No.Ce = 58).
(i) State the law which helps to determine the limiting molar conductivity of weak electrolyte.
(ii) Calculate limiting molar conductivity of CaSO₄ (limiting molar conductivity of calcium and sulphate ions are 119.0 and 160.0 Scm² mol⁻¹ respectively)
Calculate the molality of ethanol solution in which the mole fraction of water is 0.88.
What are the transition elements ? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution ?
Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction
(ii) Isotonic solutions
(iii) Van’t Hoff factor
(iv) Ideal solution
Why a mixture of Carbon disulphide and acetone shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law? What type of azeotrope is formed by this mixture?
