Calculate the molality of ethanol solution in which the mole fraction of water is 0.88.
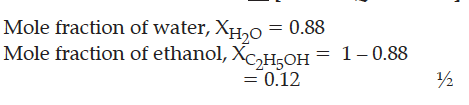

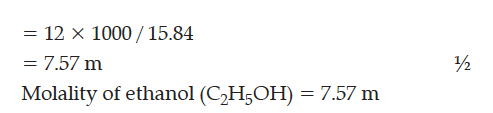
The following curve is obtained when molar conductivity is plotted against the square root of concentration, c½ for two electrolytes A and B :
Explain why :
(i) E° for Mn³⁺/Mn²⁺ couple is more positive than that for Fe³⁺/Fe²⁺. (At. Nos. Mn = 25, Fe = 26).
(ii) Ce³⁺ can be easily oxidized to Ce⁴⁺. (At. No.Ce = 58).
What is meant by ‘disproportionation’ ? Give an example of a disproportionation reaction in aqueous solution.
In the following ions:
Mn³⁺, V³⁺, Cr³⁺, Ti⁴⁺
(Atomic no: Mn = 25, V = 23, Cr = 24, Ti = 22)
(a) Which ion is most stable in an aqueous solution?
(b) Which ion is the strongest oxidizing agent?
(c) Which ion is colourless?
(d) Which ion has the highest number of unpaired electrons?
There are two possible reactions for cathode in the electrolysis of aqueous
\(ZnCl_2\) :\(Zn^{2+}\) (aq) + 2\(e^-\) → Zn(s) \(E^0\) = -0.76 V
2\(H_2\)O (l) + 2\(e^-\) → H2 (g) + 2\(OH^-\) (aq) \(E^0\) = - 0.83 V
Which one will take place? Why?
A 1.00 molar aqueous solution of trichloroacetic acid (CCl₃COOH) is heated to its boiling point. The solution has the boiling point of 100.18 °C. Determine the van’t Hoff factor for trichloroacetic acid. ( for water = 0.512 K kg mol⁻¹).
What is meant by elevation in boiling point? Why is it a colligative property?
