Derive expression for Raoult’s law when the solute is non-volatile.
Raoult’s law for solution of non-volatile solution :
The relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to the mole fraction of solute when solvent alone is volatile.
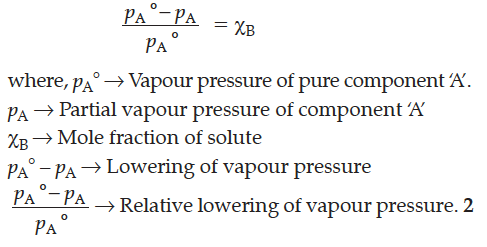
The relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to the mole fraction of solute when solvent alone is volatile.
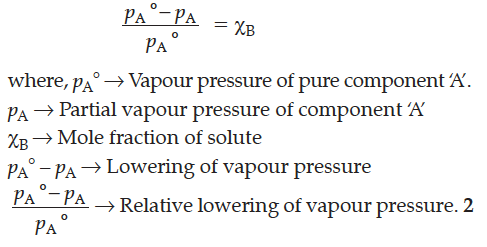
The following curve is obtained when molar conductivity is plotted against the square root of concentration, c½ for two electrolytes A and B :
Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction (x)
(ii) Molality of a solution (m)
What is meant by ‘disproportionation’ ? Give an example of a disproportionation reaction in aqueous solution.
(i) Write the colligative property which is used to find the molecular mass of macromolecules.
(ii) In non-ideal solution, what type of deviation shows the formation of minimum boiling azeotropes?
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 Scm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Following reactions can occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous silver nitrate solution using Pt electrodes:
State Raoult’s law for the solution containing volatile components. What is the similarity between Raoult’s law and Henry’s law ?
