Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction
(ii) Isotonic solutions
(iii) Van’t Hoff factor
(iv) Ideal solution
(i) Mole fraction
(ii) Isotonic solutions
(iii) Van’t Hoff factor
(iv) Ideal solution
(i) Mole fraction is the ratio of number of moles of one component to the total number of moles in a mixture.
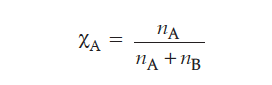
where = number of moles of component A.
= number of moles of component B.
(ii) Two solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
(iii) Van’t Hoff factor is the ratio of normal molecular mass and observed molecular mass.
(iv) Ideal solution : The solution which follows Raoult’s law over entire range of concentrations at specific temperature is called ideal solution.
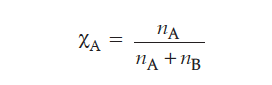
where = number of moles of component A.
= number of moles of component B.
(ii) Two solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
(iii) Van’t Hoff factor is the ratio of normal molecular mass and observed molecular mass.
(iv) Ideal solution : The solution which follows Raoult’s law over entire range of concentrations at specific temperature is called ideal solution.
Calculate the molality of ethanol solution in which the mole fraction of water is 0.88.
The conductivity of metals decreases while that of electrolytes increases with increase in temperature. Why?
When chromite ore FeCr₂O₄ is fused with NaOH in presence of air, a yellow coloured compound
(A) is obtained which on acidification with dilute sulphuric acid gives a compound (B). Compound (B) on reaction with KCl forms a orange coloured crystalline compound (C).
(i) Write the formulae of the compounds (A), (B) and (C).
(ii) Write one use of compound (C).
What are the transition elements ? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equations for its reaction with (i) an iodide (ii) H₂S.
Define azeotropes. What type of azeotrope is formed by positive deviation from Raoult’s law ?
Give an example.
Define the following terms:
(i) Abnormal molar mass
(ii) van’t Hoff factor
