Equal potentials are applied on an iron and copper wire of same length. In order to have same current flow in the wire, the ratio 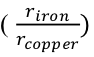 ( of their radii must be [Given that specific resistance of iron = 1.0 × 10⁻⁷ Ωm and that of copper = 1.7 × 10⁻⁸ Ωm]
( of their radii must be [Given that specific resistance of iron = 1.0 × 10⁻⁷ Ωm and that of copper = 1.7 × 10⁻⁸ Ωm]
(a) About 1.2
(b) About 2.4
(c) About 3.6
(d) About 4.8
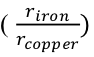
(a) About 1.2
(b) About 2.4
(c) About 3.6
(d) About 4.8
(b) About 2.4
A new flashlight cell of emf 1.5 volts gives a current of 15 amps, when connected directly to an ammeter of resistance 0.04 Ω. The internal resistance of cell is
(a) 0.04 Ω
(b) 0.06 Ω
(c) 0.10 Ω
(d) 10 Ω
A Daniel cell is balanced on 125 cm length of a potentiometer wire. When the cell is short circuited with a 2 Ω resistance, the balancing length obtained is 100 cm. Internal resistance of the cell will be
(a) 1.5 Ω
(b) 0.5 Ω
(c) 1.25 Ω
(d) 4/5 Ω
Length of a hollow tube is 5 m, its outer diameter is 10 cm and thickness of its wall is 5 mm. If resistivity of the material of the tube is 1.7 x 10⁻⁸ Ωm, then the resistance of the tube will be
(a) 5.6 × 10⁻⁵ Ω
(b) 2 × 10⁻⁵ Ω
(c) 4 × 10⁻⁵ Ω
(d) None of these
In meter bridge, the balancing length from left end when standard resistance of 1 Ω is in right gap is found to be 20 cm. The value of unknown resistance is
(a) 0.25 Ω
(b) 0.4 Ω
(c) 0.5 Ω
(d) 4 Ω
A network of resistors is connected to a 16 V battery with internal resistance of 1Ω as shown in the Fig. Compute the equivalent resistance of the network.
(a) 5 ohm
(b) 7 ohm
(c) 9 ohm
(d) 10 ohm
A torch bulb rated as 4.5 W, 1.5 V is connected as shown in the figure. The emf of the cell needed to make the bulb glow at full intensity is
(a) 4.5 V
(b) 1.5 V
(c) 2.67 V
(d) 13.5 V
Five resistances are combined according to the figure. The equivalent resistances between the points X and Y will be
(a) 10 Ω
(b) 22 Ω
(c) 20 Ω
(d) 50 Ω
The potential energy of a charged parallel plate capacitor is \(U_0\). If a slab of dielectric constant K is inserted between the plates, then new potential energy will be
(a) \(U_0\)/K
(b) \(U_0\)K²
(c) \(U_0\)/K²
(d) \(U_0\)²
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities I and 41 superimpose. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are:
(a) 5I and I
(b) 5I and 3I
(c) 3I and I
(d) 9I and I
The figure below shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.40 Ω maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire AB. A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of 1.04 V (for very moderate currents up to a few mA) gives a balance point at 67.3 cm length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, a very high resistance of 600 KΩ is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown emf Ꜫ and the balance point, found similarly, turns out to be at 82.3 cm length of the wire. What is the value Ꜫ?
(a) 0.25 V
(b) 2.25 V
(c) 3.25 V
(d) 1.25 V
Equipotential surfaces at a great distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are approximately
(a) spheres
(b) planes
(c) paraboloids
(d) ellipsoids
A small signal voltage V(t) = V₀ sin(ωt) is applied across an ideal capacitor C
(a) Current I(t) is in phase with voltage V(t).
(b) Current I(t) leads voltage V(t) by 180°.
(c) Current I(t), lags voltage V(t) by 90°.
(d) Over a full cycle the capacitor C does not consume any energy from the voltage source
The amount of work required to increase the distance between -6µC and 4µC from 6 cm to 18 cm will be :
(a) 1.8 J
(b) 2.4 J
(c) 1.8 µJ
(d) 2.4 µJ
Minimum number of capacitor of 2μF each required to obtain a capacitance of 5μF will be:
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 6
