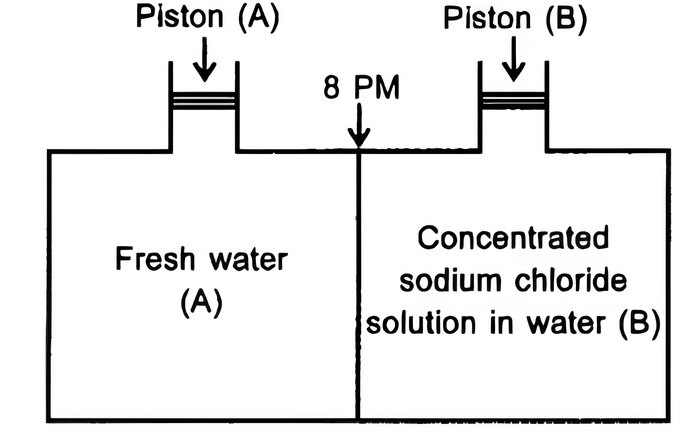
Consider the figure and mark the correct option.
(a) water will move from side (A) to side (B) if a pressure lower than osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
(b) water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure greater than osmotic , pressure is applied on piston (B).
(c) water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
(d) water will move from side (A) to side (B) if pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (A).
(a) water will move from side (A) to side (B) if a pressure lower than osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
(b) water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure greater than osmotic , pressure is applied on piston (B).
(c) water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
(d) water will move from side (A) to side (B) if pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (A).

(b) water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure greater than osmotic , pressure is applied on piston (B).
Assertion: Cooking time is reduced in pressure cooker.
Reason: Boiling point of water inside the pressure cooker is lowered.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
Assertion: An aqueous solution of NaCl freezes below 273 K.
Reason: Vapour pressure of the solution is less than that of the pure solvent.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
Assertion: Molarity of the solution changes with temperature.
Reason: Molarity is a colligative property.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
Assertion: Isotonic solutions do not show any osmosis when placed side by side.
Reason: Isotonic solutions have same solute concentration.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
(a) 30 g of urea (M = 60 g mol-1) is dissolved in 846 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution if vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg.
(b) Write two differences between ideal solutions and non-ideal solutions.
Low concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitude is due to-
(a) low temperature
(b) low atmospheric pressure
(c) high atmospheric pressure
(d) both low temperature and high atmospheric pressure
(i) Gas (A) is more soluble in water than Gas (B) at the same temperature. Which one of the two gases will have the higher value of KH (Henry’s constant) and why ?
(ii) In non-ideal solution, what type of deviation shows the formation of maximum boiling azeotropes ?
Which of the following statement is false?
a) Radon is obtained from the decay of radium
b) Helium is an inert gas
c) Xenon is the most reactive among the rare gases
d) The most abundant rare gas found in the atmosphere is helium
The decreasing order of boiling point of the following alcohols is
(a) 3-methylbuan-2-ol > 2-methylbutan-2-ol > pentan-1-ol.
(b) Pentan-1-ol > 3-methylbutan-2-ol > 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
(c) 2-methylbutan-2-ol > 3-methylbutan-2-ol > pentan-1-ol.
(d) 2-methylbutan-2-ol > pental-1-ol > 3-methylbutan-2-ol.
The order of reactivity of the following alcohols with halogen acids is
The molal elevation constant depends upon
(a) nature of solute.
(b) nature of the solvent.
(c) vapour pressure of the solution.
(d) enthalpy change.
Which of the following Defects is also known as dislocation defect?
(A) Frenkel defect
(B) Schottky defect
(C) Non-stoichiometric defect
(D) Simple interstitial defect
Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms are dropped under the curved lattice of metals. Which of the following is not the characteristics property of interstitial compounds?
(A) They have high melting points in to pure metals
(B) They are very hard
(C) They retain metallic Conductivity
(D) They are chemically very reactive
Which of the following is not true about the ionic solids?
(A) Bigger ions form the close packed structure.
(B) Smaller ions occupy either the tetrahedral or the octahedral voids depending upon their size.
(C) Occupation of all the voids is not necessary.
(D) The fraction of octahedral or tetrahedral voids occupied depends upon the radii of the ions occupying the voids.
