The properties of the solutions which depend only on the number of solute particles but not on the nature of the solute are called colligative properties. Relative lowering in vapour pressure is also an example of colligative properties. For an experiment, sugar solution is prepared for which lowering in vapour pressure was found to be 0.061 mm of Hg.(vapour pressure of water at \(20^\circ\)C is 17.5 mm of Hg).
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
(i) Relative lowering of vapour pressure for the given solution is-
(a) 0.00348
(b) 0.061
(c) 0.122
(d) 1.75
(ii) The vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of Solution will be
(a) 17.5
(b) 0.61
(c) 17.439
(d) 0.00348
(iii) Mole fraction of sugar in the solution is
(a) 0.00348
(b) 0.9965
(c) 0.061
(d) 1.75
(iv) If weight of sugar taken is 5 g in 108 g of water then molar mass of sugar will be
(a) 358
(b) 120
(c) 240
(d) 400
(v) The vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of water at 293 K when 25 g of glucose is dissolved in 450 g of water is
(a) 17.2
(b) 17.4
(c) 17.120
(d) 17.02
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
(i) Relative lowering of vapour pressure for the given solution is-
(a) 0.00348
(b) 0.061
(c) 0.122
(d) 1.75
(ii) The vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of Solution will be
(a) 17.5
(b) 0.61
(c) 17.439
(d) 0.00348
(iii) Mole fraction of sugar in the solution is
(a) 0.00348
(b) 0.9965
(c) 0.061
(d) 1.75
(iv) If weight of sugar taken is 5 g in 108 g of water then molar mass of sugar will be
(a) 358
(b) 120
(c) 240
(d) 400
(v) The vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of water at 293 K when 25 g of glucose is dissolved in 450 g of water is
(a) 17.2
(b) 17.4
(c) 17.120
(d) 17.02
(i) (a) 0.00348.

(ii) (c) 17.439.
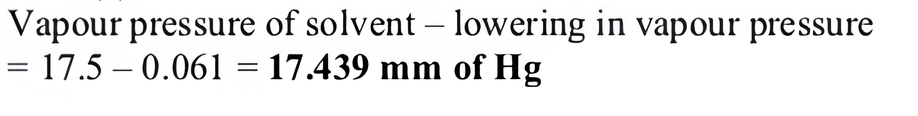
(iii) (a) 0.00348.
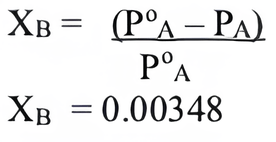
(iv) (c) 240.
(v) (b) 17.4.
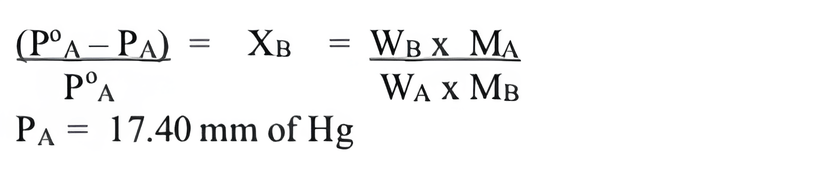

(ii) (c) 17.439.
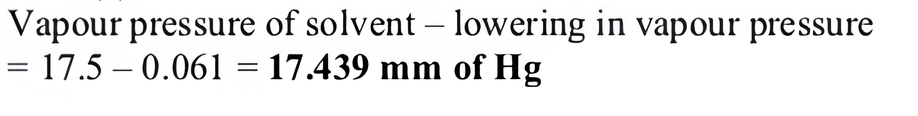
(iii) (a) 0.00348.
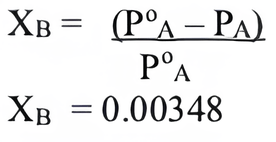
(iv) (c) 240.
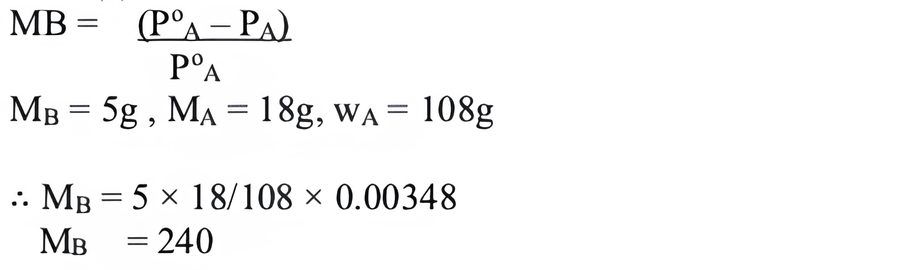
(v) (b) 17.4.
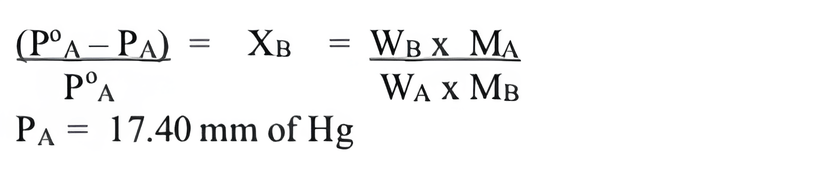
Consider the figure and mark the correct option.
(a) water will move from side (A) to side (B) if a pressure lower than osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
(b) water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure greater than osmotic , pressure is applied on piston (B).
(c) water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
(d) water will move from side (A) to side (B) if pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (A).
Acetone and carbon disulphide form binary liquid solution showing positive deviation from Raoult’s law. The normal boiling point (Tb) of pure acetone is less than that of pure \(CS_2\). Pick out the
incorrect statement among the following-
(a) Boiling temperature of the mixture is always less than the boiling temperature of acetone
(b) Boiling temperature of Azeotropic mixture is always less than the boiling temperature of acetone
(c) When a small amount of \(CS_2\) (less volatile component) is added to an excess of acetone boiling point
of the resulting mixture increases
(d) A mixture of \(CS_2\) and \(CH_3\)\(COCH_3\) can be completely separated by simple fractional distillation
Assertion: 1 M glucose will have a higher boiling point than 2 M glucose.
Reason: Elevation in boiling point is a colligative property which depends upon the number of particles of solute in the solution.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
Assertion: Molarity of the solution changes with temperature.
Reason: Molarity is a colligative property.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
Assertion: An aqueous solution of NaCl freezes below 273 K.
Reason: Vapour pressure of the solution is less than that of the pure solvent.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
Assertion: Cooking time is reduced in pressure cooker.
Reason: Boiling point of water inside the pressure cooker is lowered.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
Assertion: Isotonic solutions do not show any osmosis when placed side by side.
Reason: Isotonic solutions have same solute concentration.
A. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of Assertion .
B. If both Assertion and Reason are correct and reason is not correct explanation of Assertion
C. If Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. If Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct.
Group 18 elements are called noble gases and not inert gases because compounds of Kr, Xe and Rn have been prepared. Their general electronic configuration is \(ns^2\)\(np^6\) except He(\(1s^2\) ). They have highest ionisation enthalpy and positive electron gain enthalpy due to stable electronic configuration. Helium is found in sun and stars. Noble gases have low boiling points due to weak van der Waals’ forces of attraction. Xenon forms \(XeF_2\), \(XeF_4\), \(XeF_6\), \(XeOF_4\), \(XeO_3\), \(XeO_2\)\(F_2\), their structures can be drawn on bases of VSEPR theory. Helium is mixed with oxygen by deep sea divers to avoid pain. Neon is used in coloured advertising lights. Argon is used in bulbs as inert gas. Kr and Xe are used in high efficiency lamps, head light of cars. Radon is radioactive formed by a-decay of Radium 226 88Ra Argon is most abundant (0.9%) noble gas in atmosphere.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer.
1) What are the elements in group 18 (the far right) of the periodic table called?
a) Alkali metals
b) Alkaline earth metals
c) Halogens
d) Noble gases
2) Out of (i) \(XeO_3\) (ii) \(XeOF_4\) and (iii) \(XeF_6\) , the molecules having the same number of lone pairs on Xe are -
a) (i) and (ii) only
b) (i) and (iii) only
c) (ii) and (iii) only
d) (i) , (ii) and (iii)
3) Which one has linear shape?
a) \(XeF_2\)
b) \(XeF_4\)
c) \(XeF_6\)
d) \(XeO_3\)
4) Which of the outer electronic configuration represent Argon?
a) \(ns^2\)\(np^4\)
b) \(ns^2\)\(np^3\)
c) \(ns^2\)\(np^6\)
d) \(ns^1\)\(np^6\)
5) Which of the following statement is false?
a) Radon is obtained from the decay of radium
b) Helium is an inert gas
c) Xenon is the most reactive among the rare gases
d) The most abundant rare gas found in the atmosphere is helium
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl halides are prepared by the free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes, replacement of -OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arene. Fluorine and iodides are best prepared by halogen exchange method. These compounds find wide applications in industry as well as in day-to-day life. These compounds are generally used as solvents and as starting material for the synthesis of a large number of organic compounds.
(i) The best method for the conversion of an alcohol into analkyl chloride is by treating the alcohol with
(a) \(PCl_5\)
(b) dry HCl in the presence of anhydrous \(ZnCl_2\)
(c) \(SOCl_2\) in presence of pyridine
(d) None of these
(ii) The catalyst used in the preparation of an alkyl chloride bythe action of dry HCl on an alcohol is
(a) anhydrous \(AlCl_3\)
(b) \(FeCl_3\)
(c) anhydrous \(ZnCl_2\)
(d) Cu
(iii) An alkyl halide reacts with metallic sodium in dry ether. The reaction is known as :
(a) Frankland’sreaction
(b) Sandmeyer’sreaction
(c) Wurtz reaction
(d) Kolbe’s reaction
(iv) Fluorobenzene (\(C_6\)\(H_5\)F) can be synthesized in the laboratory
(a) by direct fluorination of benzene with \(F_2\) gas
(b) by reacting bromobenzene with NaF solution
(c) by heating phenol with HF and KF
(d) from aniline by diazotisation followed by heating thediazonium salt with \(HBF_4\)
(v) When 2-bromobutane reacts with alcoholic KOH, thereaction is called
(a) halogenation
(b) chlorination
(c) hydrogenation
(d) dehydrohalogenation
Boiling point or freezing point of liquid solution would be affected by the dissolved solids in the liquid phase. A soluble solid in solution has the effect of raising its boiling point and depressing its freezing point. The addition of non-volatile substances to a solvent decreases the vapor pressure and the added solute particles affect the formation of pure solvent crystals. According to many researches the decrease in freezing point directly correlated to the concentration of solutes dissolved in the solvent. This phenomenon is expressed as freezing point depression and it is useful for several applications such as freeze concentration of liquid food and to find the molar mass of an unknown solute in the solution. Freeze concentration is a high quality liquid food concentration method where water is removed by forming ice crystals. This is done by cooling the liquid food below the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point depression is referred as a colligative property and it is proportional to the molar concentration of the solution (m), along with vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure. These are physical characteristics of solutions that depend only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute. The characters are not depending on the solute’s identity.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
(i) When a non volatile solid is added to pure water it will-
(a) boil above \(100^\circ\)C and freeze above \(0^\circ\)C.
(b) b) boil below \(100^\circ\)C and freeze above \(0^\circ\)C.
(c) boil above \(100^\circ\)C and freeze below \(0^\circ\)C.
(d) boil below \(100^\circ\)C and freeze below \(0^\circ\)C.
(ii) Colligative properties are
(a) dependent only on the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s and solute’s
identity.
(b) dependent only on the identity of the solute and the concentration of the solute and independent
of the solvent’s identity.
(c) dependent on the identity of the solvent and solute and thus on the concentration of the solute.
(d) dependent only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute and independent
of the solute’s identity.
(iii) Assume three samples of juices A, B and C have glucose as the only sugar present in them. The concentration of sample A, B and C are 0.1 M, 0.5 M and 0.2 M respectively. Freezing point will be highest for the fruit juice
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) all have same freezing point
(iv) Identify which of the following is a colligative property?
(a) Freezing point
(b) Boiling point
(c) Osmotic pressure
(d) All of the above
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The transition metals when exposed to oxygen at low and intermediate temperatures form thin, protective oxide films of up to some thousands of Angstroms in thickness. Transition metal oxides lie between the extremes of ionic and covalent binary compounds formed by elements from the left or right side of the periodic table. They range from metallic to semiconducting and deviate by both large and small degrees from stoichiometry. Since d electron bonding levels are involved, the cations exist in various valence states and hence give rise to a large number of oxides. The crystal structures are often classified by considering a cubic or hexagonal close-packed lattice of one set of ions with the other set of ions filling the octahedral or tetrahedral interstices. The actual oxide structures, however, generally show departures from such regular arrays due in part to distortions caused by packing of ions of different size and to ligand field effects. These distortions depend not only on the number of d-electrons but also on the valence and the position of the transition metal in a period or group.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above
passage.
A. Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
B. Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
C. Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
D. Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
1) Assertion: Cations of transition elements occur in various valence states
Reason: Large number of oxides of transition elements are possible.
2) Assertion: Crystal structure of oxides of transition metals often show defects.
Reason: Ligand field effect cause distortions in crystal structures.
3) Assertion : Transition metals form protective oxide films.
Reason: Oxides of transition metals are always stoichiometric.
4) Assertion: CrO crystallises in a hexagonal close-packed array of oxide ions with two out of every three octahedral holes occupied by chromium ions.
Reason: Transition metal oxide may be hexagonal close-packed lattice of oxide ions with metal ions filling the octahedral voids.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All real structures are three-dimensional structures. They can be obtained by stacking two dimensional layers one above the other while placing the second square close packed layer above the first we follow the same rule that was followed when one row was placed adjacent to the other. The second layer is placed over the first layer such that the spheres of the upper layer are exactly above there of the first layer. In his arrangement spheres of both the layers are perfectly aligned horizontally as well as vertically. A metallic element crystallise into a lattice having a ABC ABC pattern and packing of spheres
leaves out voids in the lattice.
1) What type of structure is formed by this arrangement?
(A) ccp
(B) hcp
(C) ccp/fcc
(D) none of the above
2) Name the non-stoichiometric point defect responsible for colour in alkali metal halides.
(A) Frenkel defect
(B) Interstitial defect
(C) Schottky defect
(D) F-centres
3) What is the total volume of atoms in a face centred cubic unit cell of a metal? (r is atomic radius).
(A) 16/3 \(πr^3\)
(B) \(πr^3\)
(C) 24/3 \(πr^3\)
(D) 12/3 \(πr^3\)
4) Which of the following statements not true for the amorphous and crystalline solids?
(A) Amorphous solids are isotropic and crystalline solids are anisotropic.
(B) Amorphous solids are short range order and crystalline solids are long range order.
(C) Amorphous solids melt at characteristic temperature while crystalline solids melt over a range of temperature.
(D) Amorphous solids have irregular shape and crystalline solids have a geometrical shape.
The properties of dilute or ideal solutions which depend only upon the concentration of the solute in the solution and no other characteristics are known as colligative properties. There are in all four such properties i.e. relative lowering in vapour pressure, osmotic pressure, elevation in boiling point temperature and depression in freezing point temperature. All of them help in calculating the observed molar mass of the solute which is inversely proportional to the colligative property involved. Out of these, osmotic pressure may be regarded as the best for the determination of molecular mass of the solute. According to Van’t Hoff theory of dilute solution, π = CRT, where ‘π’ is the osmotic pressure while ‘C’ is the molar concentration of the solution.
(i) When liquids A and B are mixed, hydrogen bonding occurs. The solutions will show:
a) Positive deviation from Raoult’s law
b) Negative deviation from Raoult’s law
c) No deviation from Raoult’s law
d) Slightly increase in volume
(ii) The azeotropic mixture of water and HCl boils at \(108.5^\circ\)C when the mixture is distilled. It is possible to obtain:
a) Pure HCl
b) Pure water
c) Pure water as well as pure HCl
d) Neither HCl nor water in their pure states.
(iii) On freezing an aqueous solution of sugar, the solid which starts separating out is:
a. Sugar
b. Ice
c. Solution with the same composition
d. Solution with different composition
(iv) The value of osmotic pressure does not depend upon:
a) Concentration of the solution
b) Temperature of the solution
c) Number of the particles of the solute present
d) Structure of the solute particles
(v) Effect of adding a non-volatile solute to a solvent is :
a) to lower the vapour pressure
b) to increase the freezing point
c) to decrease the boiling point
d) to decrease the osmotic pressure
Proteins are high molecular mass complex biomolecules of amino acid The important proteins required for our body are enzymes, hormones, antibodies, transport proteins, structural proteins, contractile proteins etc. Except for glycine, all o-amino acids have chiral carbon atom and most of them have L-configuration. The amino acids exists as dipolar ion called zwitter ion, in which a proton goes from the carboxyl group to the amino group. A large number of-amino acids are joined by peptide bonds forming polypeptides. The peptides having very large molecular mass (more than 10,000) are called proteins. The structure of proteins is described as primary structure giving sequence of linking of amino acids; secondary structure giving manner in which polypeptide chains are arranged and folded; tertiary structure giving folding, coiling or bonding polypeptide chains producing three dimensional structures and quaternary structure giving arrangement of sub- units in an aggregate protein molecule.
In these questions (Q. No. i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
i) Assertion .- All amino acids are optimally active.
Reason : Amino acids contain asymmetric carbon atoms.
ii) Assertion .- In o-helix structure, intramolecular H-bonding takes place whereas in β-pleated structure,intermolecular H-bonding takes place.
Reason : An egg contains a soluble globular protein called albumin which is present in the white part.
iii) Assertion .- Secondary structure of protein refers to regular folding patterns of continuous portions of the polypeptide chain
Reason : Out of 20 amino acids, only 12 amino acids can be synthesized by human body.
iv) Assertion .- The. helical structure of protein is stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bond between —NH and carbonyl oxygen.
Reason : Sanger’s reagent is used for the identification of N-terminal amino acid of peptide chain.
