Figure shows the field lines due to a positive charge. Is the work done by the field in moving a small positive charge from Q to P, positive or negative? Give reason.
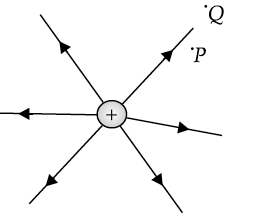

Negative,
This happens as the charge is displaced against the force exerted by the field.
This happens as the charge is displaced against the force exerted by the field.
Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point ? Give reason.
A point charge +Q is placed at point O as shown in the figure. Is the potential difference – positive, negative or zero ?
Why are electric field lines perpendicular at a point on an equipotential surface of a conductor ?
Two point charges q and –2q are kept d distance apart. Find the location of the point relative to charge q at which potential due to this system of charges is zero.
Obtain the expression for the potential due to an electric dipole of dipole moment p at a point ‘d’ on the axial line.
The electric potential due to point charge 3 nC at distance of 9 cm is
(a) 270 v
(b) 3 v
(c) 300 v
(d) 30 v
Show variation of resistivity of copper as a function of temperature in a graph.
State which of the two a capacitor or an inductor, tends to become SHORT when the frequency of the applied alternating voltage has a high value.
Figure shows a point charge + Q, located at a distance R/2 from the centre of a spherical metal shell. Draw the electric field lines for the given system.
Nichrome and copper wires of same length and same radius are connected in series. Current I is passed through them. Which wire gets heated up more ? Justify your answer.
Why do the electric field lines never cross each other ?
Two point charges ‘q1’ and ‘q2’ are placed at a distance ‘d’ apart as shown in the figure. The electric field intensity is zero at a point ‘P’ on the line joining them as shown. Write two conclusions that you can draw from this.
Why do the electrostatic field lines not form closed loops ?
