A device ‘X’ is connected to an ac source V = V₀ sin(ωt). The variation of voltage, current and power in one complete cycle is shown in the following figure.
(i) Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle?
(ii) Identify the device ‘X’.
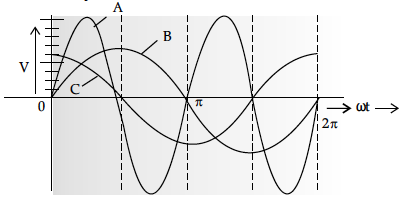
(i) Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle?
(ii) Identify the device ‘X’.

(i) A
(ii) Capacitor
Detailed Answer :
(i) Power's frequency is double of current or voltage frequency.
(ii) From the graph, the phase difference between V and I is so device ‘X’ may be an inductor (L) or capacitor (C) but since current (graph C) leads the voltage (graph B), device is capacitor.
(ii) Capacitor
Detailed Answer :
(i) Power's frequency is double of current or voltage frequency.
(ii) From the graph, the phase difference between V and I is so device ‘X’ may be an inductor (L) or capacitor (C) but since current (graph C) leads the voltage (graph B), device is capacitor.
For an ideal conductor, connected across a sinusoidal ac voltage source. State which one of the following quantity is zero :
(i) Instantaneous power
(ii) Average power over full cycle of the ac voltage source.
An ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt is applied to a pure inductor L. Obtain an expression for the current in the circuit. Prove that the average power supplied to an inductor over one complete cycle is zero.
A source of ac voltage V = V₀ sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
A lamp is connected in series with a capacitor. Predict your observation for dc and ac connections. What happens in each if the capacitance of the capacitor is reduced ?
A 40 mF capacitor is connected to a 200 V, 50 Hz ac supply. The r.m.s value of the current in the circuit is, nearly
(a) 1.7 A
(b) 2.05 A
(c) 2.5 A
(d) 25.1 A
In highly inductive load circuit, it is more dangerous when
(a) we close the switch
(b) open the switch
(c) increasing the resistance
(d) decreasing the resistance
An alternating voltage given by V = 140sin314 t is connected across a pure resistor of 50 Find :
(i) the frequency of the source.
(ii) the rms current through the resistor.
Why are electric field lines perpendicular at a point on an equipotential surface of a conductor ?
Two equal balls having equal positive charge ‘q’ coulombs are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length. What would be the effect on the force when a plastic sheet is inserted between the two ?
Graph showing the variation of current versus voltage for a material GaAs is shown in the figure, identify the region of :
A point charge Q is placed at point ‘O’ as shown in figure. Is the potential at point A, i.e., , greater, smaller or equal to potential, at point B, when Q is (i) positive, and (ii) negative charge?
Figure shows a point charge + Q, located at a distance R/2 from the centre of a spherical metal shell. Draw the electric field lines for the given system.
A charge ‘q’ is moved from a point A above a dipole of dipole moment ‘p’ to a point B below the dipole in equatorial plane without acceleration. Find the work done in the process.
