The angle of incidence at which reflected light is totally polarised for reflection from air to glass (refractive index n) is
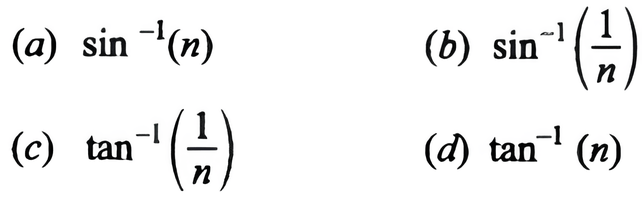
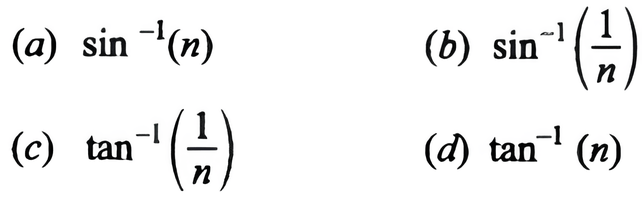
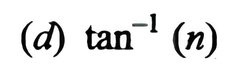
The colours on the soap bubble is due to
(a) Interference
(b) Diffraction
(c) Polarisation
(d) Reflection
Bending of Light phenomena is shown by
(a) Polarization
(b) Diffraction
(c) Interference
(d) Dispersion
The wavefront due to a source situated at infinity is
(a) spherical
(b) cylindrical
(c) planar
(d) circular
The wave-front due to source situated at the infinity is
(A) Spherical
(B) Cylindrical
(C) Plane
(D) Rectangular
Huygens theory could not explain
a. Reflection of light
b. Photoelectric effect
c. Interference of light
d. Diffraction of light
The parameter of light wave which remain same after refraction
(A) speed
(B) frequency
(C) wavelength
(D) none of these
A phase difference of 5π corresponds to a path difference (in terms of λ) of:
(a) 5λ
(b) 10λ.
(c) 5λ/2
(d) 2λ
What type of wave front will emerge from any distant source of light?
i. Spherical wave front
ii. Cylindrical wave front
iii. Plane wave front
iv. None of these
In an interference experiment, the spacing between successive maxima and minima is
(A) λd / D
(B) λD / d
(C) dD / λ
(D) λd / 4D
The angle of incidence at which reflected light is totally polarised for reflection from air to glass (refractive index n) is
To observe diffraction, the size of the obstacle
(a) should be X/2, where X is the wavelength.
(b) should be of the order of wavelength.
(c) has no relation to wavelength.
(d) should be much larger than the wavelength.
Two cables of copper are of equal lengths. One of them has a single wire of area of cross- section A, while other has 10 wires of cross-sectional area A/10 each. Give their suitability for transporting A.C. and D.C.
(a) only multiple strands for A.C., either for D.C.
(b) only multiple strands for A.C., only single strand for D.C.
(c) only single strand for D.C., either for A.C.
(d) only single strand for A.C., either for D.C.
When exposed to sunlight, thin films of oil on water often exhibit brilliant colours due to the phenomenon of
(a) interference
(b) diffraction
(c) dispersion
(d) polarization
The current sensitivity of a Galvanometer can be increased by decreasing-
a) Magnetic field B
b) No. of turns N
c) Torsional constant k
d) Area of the coil A
